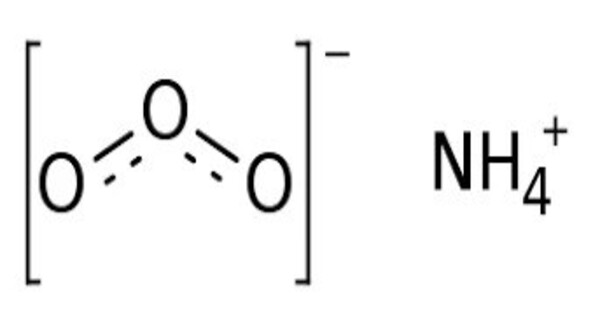Ammonium ozonide is an oxygen rich molecule containing an ammonium cation (NH4+) and an ozonide anion (O3−). Ammonium ozonide, like alkali ozonides, is a red solid. Ammonium ozonide is stable at low temperatures, but it decomposes to ammonium nitrate at temperatures above -70 °C.
Ammonium ozonide is typically unstable and can decompose explosively. Ozonides, in general, are known for their instability and potential hazards.
Preparation and decomposition
Ammonium ozonide is made by bubbling gaseous ozone through liquid ammonia at -110 °C. This method suffers from a low yield. It’s usually prepared by reacting ozone with an aqueous solution of ammonia. Its practical uses are limited due to its instability, and it’s mostly of interest in specialized chemical research.
12 NH3 + 11 O3 → 9 NH4O3 + 3 NO2
Ammonium ozonide decomposes into ammonium nitrate, oxygen gas, and water. If the above reaction is done at high temperatures, these decomposition products result immediately and no ozonide is formed.
4 NH4O3 → 2 NH4NO3 + O2 + 4 H2O
Properties
Ammonium ozonide is known to be quite unstable. Ozonides in general are reactive and can decompose explosively under certain conditions. As such, ammonium ozonide must be handled with care, typically in controlled environments. Details about its physical appearance are limited, but ozonides are often colorless or white solids. However, the instability of ammonium ozonide means it might not be easily observable in a stable form.
- Chemical formula: H4NO3
- Molar mass: 66.036 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Deep red solid
Applications
- Laboratory Synthesis: It is typically synthesized in a laboratory setting. It is not a substance that occurs naturally in significant quantities. Its preparation involves reacting ozone (O₃) with ammonium compounds.
- Research and Industrial Use: Due to its instability and the hazards associated with ozonides, ammonium ozonide is not commonly used in industrial applications. Its primary interest lies in chemical research and the study of ozonides.
Safety
Because of its explosive potential, working with ammonium ozonide requires stringent safety protocols. Researchers use special equipment and follow specific procedures to mitigate risks associated with its instability. Handling ammonium ozonide requires caution due to its explosive nature. Proper safety protocols are essential when working with or studying such compounds.