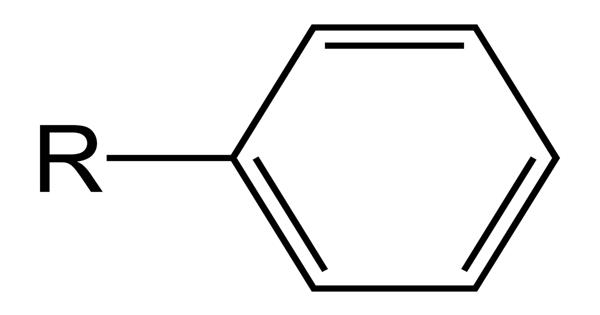
In organic chemistry, a phenyl group is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5. It is also referred to as aryl phenols, which are compounds composed of a phenolic group connected directly to another aromatic ring. Phenyl groups are closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. Any functional group containing an aromatic group, an aryl group is represented by Ar. A phenyl group is formed when a hydrogen atom is removed from the benzene ring. They are compounds composed of a phenolic group connected directly to another aromatic ring.
Properties
Phenyl groups have six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. It is a cyclic group of atoms formed when a hydrogen atom is removed from the benzene ring.
- Density: 1.248 g/mL at 25 °C
- Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass: 77.106 g/mol
- Boiling Point: 232.2±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg
- Melting Point: −30 °C
- Appearance: White crystalline solid
- Solubility: Poorly soluble in water
- Chemical Formula: C6H5
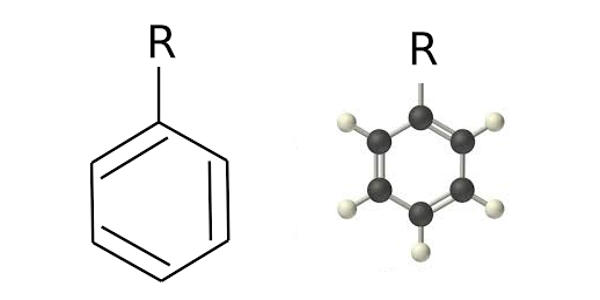
Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Aromatic phenyl group in the bridging polyene structures can improve thermo and photochemical stabilities of chromophores. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, phenyl groups are chemically aromatic and have equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Since the hydrogen atom is not present, there is a vacant point for other atoms or molecules to get attached to the phenyl group. A phenyl group is also referred to as aryl phenols.
Phenyl groups have six carbon atoms in a hexagonal planar structure, of which five are bonded to hydrogen atoms. Phenyl group as phenol reacts with bromine solution forms Bromo substituted phenol and hydrogen bromide. They are chemically aromatic and have equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. It is poorly soluble in water. The chemical equation is given below.
2C6H5OH + 5Br2 → 2C6H2Br2OH + 6HBr
Uses of Phenyl
- Used today in combination with other phenolics in various institutional and domestic disinfectant formulations.
- Used to destroy odour and promote sanitation.
- Used in public places like schools, hotels, stores and offices as a disinfectant.
- Possesses pharmacological properties and used as antioxidant, analgesics, choleretic, etc.
Information Source: