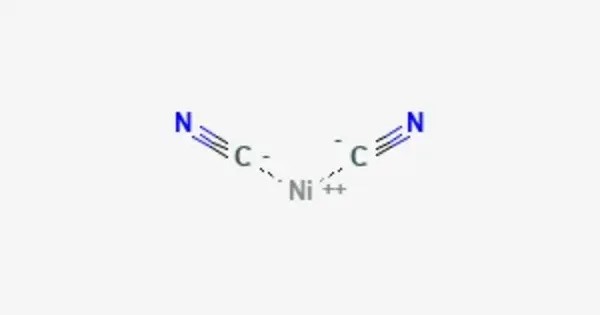
Nickel dicyanide is the inorganic compound with a chemical formula Ni(CN)2. The cyanide ions are bound to the nickel ion in a linear fashion, forming a coordination complex. It is a gray-green solid that is insoluble in most solvents. This compound is often used in electroplating, as a precursor in the production of other nickel compounds, and occasionally in other industrial processes.
Production
Addition of two equivalents of sodium or potassium cyanide to a solution of nickel(II) ions in aqueous solution leads to the precipitation of nickel(II) cyanide tetrahydrate. On heating the tetrahydrate to 140 °C, this hydrate converts to anhydrous nickel(II) cyanide.
Properties
It usually appears as a solid, which is typically white or colorless, though it can be somewhat pale depending on the specific form. It is sparingly soluble in water, but it can dissolve in acidic solutions. It is relatively stable in dry conditions but can be highly reactive in the presence of moisture or acids. The cyanide ions can be toxic, so handling should be done with care.
Chemical formula: Ni(CN)2
Molar mass: 110.729
Appearance: yellow-brown solid (dry), blue gray solid (tetrahydrate)
Chemical properties
K2[Ni(CN)4] (tetracyanonickelate) solution)
Nickel(II) cyanide dissolves in potassium cyanide solution to produce a yellowish solution containing potassium tetracyanonickelate:
Ni(CN)2 + 2 KCN → K2[Ni(CN)4]
Nickel(II) cyanide will react with dimethylglyoxime (dmgH2) and produce hydrogen cyanide:
Ni(CN)2 + 2 dmgH2 → Ni(dmgH)2 + 2 HCN
Occurrences
Nickel dicyanide doesn’t occur naturally in large quantities, but it can be synthesized in laboratories or during industrial processes. It is primarily used in:
- Electroplating: It is used in nickel electroplating, particularly when cyanide-based solutions are employed to create uniform and smooth coatings.
- Inorganic Synthesis: Nickel dicyanide may serve as a precursor or intermediate in the synthesis of other nickel compounds.
- Chemical Analysis: It can be used in certain chemical reactions or assays, including the detection of specific ions or in reactions that involve cyanide chemistry.