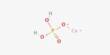
Gadolinium acetate is the acetate salt of the lanthanide element gadolinium with the chemical formula Gd(CH3COO)3. It is an inorganic coordination compound containing the rare-earth element gadolinium (Gd). It is a colorless crystal that is soluble in water and can form a hydrate. Its tetrahydrate has ground state ferromagnetism. It appears as a crystalline solid, often white to slightly off-white, and is soluble in water and polar solvents.
The compound is valued for the unique magnetic and optical properties imparted by the gadolinium ion. Gadolinium(III) has seven unpaired electrons, which makes gadolinium acetate strongly paramagnetic. This property makes it important in research on magnetic refrigeration, molecular magnets, and as a precursor in the preparation of gadolinium-based materials.
Preparation
The tetrahydrate of gadolinium acetate can be crystallized from aqueous solution by reaction of gadolinium oxide and acetic acid:
Gd2O3 + 6 HOAc + 5 H2O → [(Gd(OAc)3(H2O)2)2]·4H2O
Properties
The complex [Gd4(CH3COO)4(acac)8(H2O)4] can be obtained by the reflux reaction of gadolinium acetate and acetylacetone in the presence of triethylamine in methanol solution. It appears as a white to slightly off-white crystalline powder. The compound is soluble in water and alcohols, forming clear solutions. It has moderate thermal stability, decomposing upon heating to yield gadolinium oxide. The acetate ligands help stabilize gadolinium in solution, often used in coordination chemistry and material synthesis.
- Chemical formula: Gd(CH3COO)3
- Appearance: colorless crystal or white powder
- Density: 1.611 g·cm−3 (hydrate)
- Solubility in water: 9.7 g
Occurrences
Gadolinium acetate does not occur naturally but is synthesized in laboratories by neutralizing gadolinium oxide, hydroxide, or carbonate with acetic acid. Gadolinium itself is obtained from minerals such as monazite and bastnäsite, which contain mixed rare-earth elements. After separation and purification of gadolinium, the acetate form can be prepared for specific applications. In practice, gadolinium acetate is employed in making magnetic coordination complexes, luminescent materials, and precursors for gadolinium-based oxides and catalysts. It is also of interest in experimental studies of magnetocaloric materials and biomedical imaging agents.
Application
Gadolinium acetate serves as a starting material in the synthesis of gadolinium complexes used as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), though the acetate form itself is not directly employed clinically. It is also used in materials science, including the preparation of thin films, luminescent materials, and catalysts. In laboratory chemistry, it is studied for its coordination behavior with organic ligands. While gadolinium salts have applications in medicine and technology, safety precautions are essential, as free gadolinium ions can be toxic if not bound in stable complexes.