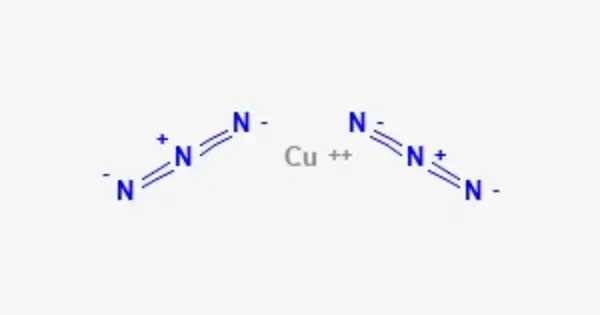
Copper(II) azide is a medium density explosive with the molecular formula Cu(N3)2. It consists of copper in the +2 oxidation state and two azide (N₃⁻) anions. Copper(II) azide is typically a yellow solid and is highly sensitive to shock, friction, and heat, which makes it a potential explosive. It is commonly used in pyrotechnics and explosives, though it requires careful handling due to its instability.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Cu(N3)2
- Molar mass: 147.586 g/mol
- Appearance: brown orthorhombic crystals
- Density: 2.6 g/cm3
- Melting point: Explodes when heated
- Stability: It is an unstable compound and can decompose explosively.
- Hazard: It is very sensitive to shock, friction, and heat, which can lead to its decomposition and the release of nitrogen gas and potentially hazardous by-products.
Uses
Copper azide is very explosive and is too sensitive for any practical use unless handled in solution.
Preparation
Copper azide can be prepared by a metathesis reaction between water-soluble sources of Cu2+ and azide ions. (Spectator ions omitted in reaction below).
Cu2+ + 2 N−3 → Cu(N3)2
It can be destroyed by concentrated nitric acid to form non-explosive products, these being nitrogen, nitrogen oxides and copper(II) nitrate.
Occurrences
Copper(II) azide is not commonly found in nature as a mineral or naturally occurring compound. However, it is synthesized in laboratories for various industrial and research purposes. Some common uses and contexts in which copper(II) azide may occur include:
Pyrotechnics and Explosives: It is used in the production of initiators or detonators in explosives. Azides are commonly used in these applications due to their high sensitivity and energy release upon decomposition.
Chemical Research: Copper(II) azide can be used in chemical reactions, particularly in the synthesis of other azide-containing compounds or in the study of metal-azide coordination complexes.
Fuel or Propellant Applications: In specialized fields, copper(II) azide can be involved in the development of certain types of propellants or fuels where the decomposition of the azide releases energy.
Safety Considerations
Handling and Storage: Copper(II) azide should be handled with care, as it is a sensitive compound. It is typically stored in small quantities in well-ventilated areas, away from heat sources, shock, and friction.
Decomposition: During decomposition, it may release toxic gases like nitrogen oxides. Proper ventilation and safety equipment (such as fume hoods) are essential when working with copper(II) azide.