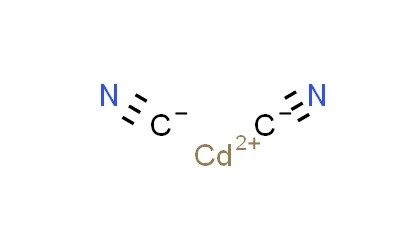
Cadmium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(CN)2. It is a cadmium salt of cyanide and is known for being highly toxic due to the presence of both cadmium and cyanide ions. It is a white crystalline compound that is used in electroplating. It is very toxic, along with other cadmium and cyanide compounds. It is typically encountered as a white crystalline solid. It can form complexes due to the nature of the cyanide ion.
Both cadmium and cyanide are toxic to humans and the environment. Cadmium exposure can lead to serious health issues, including kidney damage and bone fragility. Cyanide can disrupt cellular respiration and is potentially lethal in small doses.
Properties
It is soluble in water and can hydrolyze to form cadmium hydroxide and cyanide ion in aqueous solutions. It can react with acids, releasing hydrogen cyanide gas, which is highly toxic.
- Chemical formula: Cd(CN)2
- Molar mass: 164.45 g/mol
- Appearance: white cubic crystals
- Density: 2.226 g/cm3
- Solubility in water: 1.71 g/100 mL (15 °C), 2.2 g/100 mL (20 °C)
- Solubility: slightly soluble in alcohol, dissolves in alkali, metal cyanides and hydroxides
Preparation and structure
Cadmium cyanide is prepared commercially by treating cadmium hydroxide with hydrogen cyanide:
Cd(OH)2 + 2 HCN → Cd(CN)2 + 2 H2O
It can also be generated from tetracyanocadmate:
[Cd(CN)4]2− + CdCl2 → 2 Cd(CN)2 + 2 Cl−
Natural Sources
Cadmium is not found in nature as a free metal; it occurs primarily in minerals associated with zinc. Cadmium cyanide itself is not typically found in nature but can be generated in industrial processes.
Industrial Production:
Cadmium cyanide is produced as a byproduct in processes involving cadmium, such as electroplating and the production of certain pigments.
Uses
It is used as an electrolyte for electrodeposition of thin metallic cadmium coatings on metal to protect against corrosion. Due to its properties, it has been used in some applications, such as electroplating and as a reagent in chemical synthesis. However, due to its toxicity, its use is heavily regulated.
Handling and Safety
Due to its high toxicity, strict safety measures are essential when handling cadmium cyanide. This includes using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), working in well-ventilated areas, and following regulatory guidelines for hazardous materials.