The atom is the basic unit of matter. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains all of the chemical properties of an element. There are many different types of atoms, each with its own name, atomic mass, and size. These different atoms are called chemical elements. Atoms combine to form molecules, which then interact to form solids, gases, or liquids. The chemical elements are organized on the periodic table. Examples of elements are hydrogen and gold.
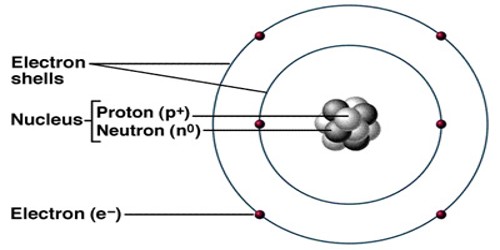
Atoms are very small, but the exact size depends on the element. Atoms range from 0.1 to 0.5 nanometers in width. One nanometer is about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. This makes atoms impossible to see without special tools. Atoms consist of three basic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. Atoms are made up of three kinds of smaller particles, called protons (which are positively charged), neutrons (which have no charge) and electrons (which are negatively charged). The protons and neutrons are heavier and stay in the middle of the atom. They are called the nucleus. They are surrounded by a cloud of electrons which are very lightweight.
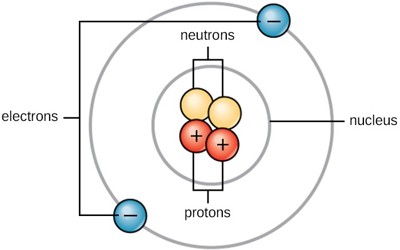
Atoms are the basic units of matter and the defining structure of elements. Atoms join together to make molecules: for example, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom combine to make a water molecule. Water is composed of hydrogen and oxygen atoms that have combined to form water molecules. When atoms join together it is called a chemical reaction.
The number of protons and electrons an atom has tells us what element it is. Hydrogen, for example, has one proton and one electron; the element sulfur has 16 protons and 16 electrons. The number of protons in the atomic number. Except for hydrogen, the nucleus also has neutrons. All atoms are electrically neutral because every atom has an equal number of electrons and protons. The number of protons and neutrons together is the atomic weight.
Most of the atom’s volume holds the electron cloud, whose mass is tiny. Atoms move faster when they are in their gas form than they do in liquid form and solid matter. In solid materials, the atoms are tightly packed next to each other so they vibrate, but are not able to move (there is no room) as atoms in liquids do. An atom’s chemical behavior is determined by the arrangement of its electrons. They may also ionize to form ionic compounds.