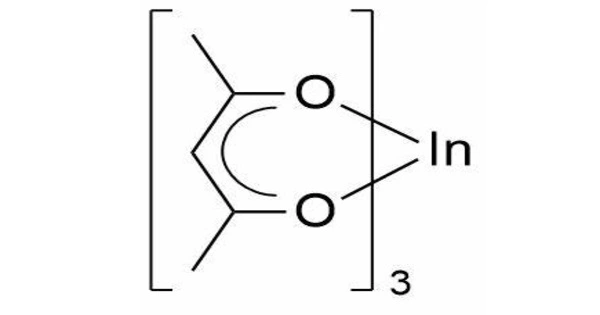
Indium acetylacetonate, often known as In(acac)3, is a chemical with the formula In(C5H7O2)3. It is a colorless solid. It has an octahedral structure. It is a coordination complex composed of an indium(III) ion (In3+) coupled to three acetylacetonate ligands. Acetylacetonate is a bidentate ligand produced from the chemical molecule acetylacetone (pentane-2,4-dione).
Indium acetylacetonate has a wide range of uses, most notably in materials science and chemistry. It is frequently used as a precursor for the deposition of indium-containing thin films in semiconductor device fabrication and solar cell manufacturing. The compound is well-known for its function in the formation of thin films of indium-containing materials via chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and atomic layer deposition (ALD) methods.
Properties
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight is approximately 515.4 g/mol.
- Appearance: It is typically a yellow to orange solid, often found as a powder or crystals.
- Melting Point: It has a melting point around 280-300°C.
- Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in water but is soluble in a variety of organic solvents, such as acetone, chloroform, and benzene.
- Coordination Geometry: It is a coordination complex with a central indium ion (In3+) coordinated by three acetylacetonate ligands (acac, C5H7O2−), resulting in a distorted octahedral geometry.
- Stability: It is thermally stable and can be used as a precursor for the deposition of indium-containing thin films, such as in semiconductor manufacturing.
Uses
Using an atmosphericpressure chemical vapor deposition approach, indium acetylacetonate and tin(II) acetylacetonate can be used to create indium tin oxide thin films. With a thickness of roughly 200 nanometers, the resulting thin films are transparent and conductive.
Indium acetylacetonate can also be used to make copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS). Thin-film CIGS solar cells are created using atomic layer chemical vapour deposition (ALCVD) and In(acac)3. It is a critical reagent in organometallic chemistry and has vital applications in the creation of new materials and technology.