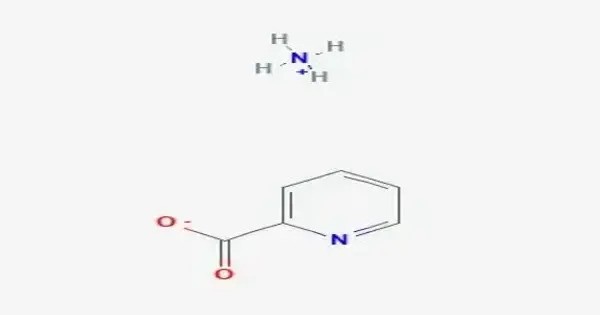
Ammonium picolinate is an organic chemical compound. This is an organic ammonium salt of picolinic acid with the chemical formula C6H8N2O2. It is an organic salt formed from picolinic acid (a carboxylic acid derived from pyridine-2-carboxylic acid) and ammonium ion. The compound is generally obtained by neutralizing picolinic acid with ammonia, yielding a crystalline salt that is moderately soluble in water.
Organic ammonium salts are generally water-soluble, though specific solubility data for ammonium picolinate are not explicitly documented. Structurally, the molecule features a pyridine ring with a carboxylate group bound to an ammonium cation, which provides ionic stabilization. This salt is less volatile and more stable compared to free picolinic acid. It is known for acting as a ligand in coordination chemistry, where the picolinate anion can chelate metal ions, enhancing their solubility and bioavailability.
Properties
Ammonium picolinate has attracted interest in biochemical and nutritional research, as derivatives of picolinic acid are involved in metal ion transport and metabolism in biological systems. Its chelating properties make it useful in forming complexes with metals such as zinc, chromium, and iron.
- Chemical formula: C6H8N2O2
- Molar mass: 140.142 g·mol−1
It typically appears as a crystalline solid or powder, highly soluble in water due to the ionic nature of the ammonium and picolinate ions. It is stable under normal conditions but may decompose when heated strongly, releasing nitrogen oxides and other gases. Being derived from picolinic acid, it retains some chelating ability, meaning it can bind to metal ions. Its molecular structure involves the protonated ammonium cation and the picolinate anion, which contains a nitrogen atom in the aromatic ring and a carboxylate group.
Occurrences
Ammonium picolinate is not commonly found in nature but can be synthesized in laboratories by neutralizing picolinic acid with ammonia. Picolinic acid itself is a natural metabolite in humans, formed through the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism. The ammonium salt, however, is mainly of interest in research and potential industrial use, rather than being a naturally occurring compound. It may appear in experimental studies related to coordination chemistry, metal ion transport, or nutritional biochemistry.
Uses
As a chelating agent, the compound may stabilize metal complexes in catalytic or industrial processes.
While not widely used in bulk industries, ammonium picolinate has niche applications in pharmaceutical research, catalysis, and analytical chemistry. Safety data are limited, but like many ammonium salts, it should be handled with care, avoiding excessive ingestion or inhalation.