Against Cash:
¨ The Customer is asked to complete a form (No. Sf-18) which is treated as an application as well as credit voucher for H.O. Account (Br. Concern).
¨ Commission Charges are calculated and inserted in the form.
¨ The voucher than given to the customer to deposit the amount.
¨ The cashier receives the cash and delivered the voucher to the remittance department against initial in his book.
¨ Then the draft is prepared and entered in the D.D. issue register. The amount of the draft is protected by the ‘protect to graph’. Then the draft No. is written of the voucher.
¨ Draft book and the voucher along with register are sent to officer in charge of the remittance department for parth-11 test, verification and signature.
¨ The draft and the voucher are sent to general section head for part-1 test and signature.
¨ Then a memorandum is issued to the customer if be desires so.
Payment of D.D.:
The followings should be checked before payment of D.D.:
¨ D.D. is drawn on the branch.
¨ Issuing branch’s rubber stamp is fixed.
¨ Amount in word & the amount in figure should be same.
¨ Verify the test number is tested.
¨ The payee must be properly identified in case of cash payment.
¨ If D.D is placed before arrival of ‘IBA’ then make the payment by debiting.
¨ Suspense A/C. D.D paid without advice, Advice will come than.
¨ Particulars of D.D payable & D.D. Paid without advice is entered in the respective register.
Charges taken for the draft:
Tk. 50.00 as postage charge is taken and 0.15% commission on the draft value. The amount is separately credited to the concern income account
Cancellation of Demand Draft:
To cancel an issued D.D. the client has to submit an application. Issuing branch then sends an I.B.D.A (inter branch debit advice to the drawn branch against previously issued I.B.C.A (inter branch credit advice).
¨ Pay Order:
If any person wants to transfer money within the local areas where the bank located then the transfer be made by ‘Pay Order’ Deference between ‘Pay Order’ and ‘Demand Draft’ is in terms of place only. Pay order is issued for remitting money within the city whereas D.D. is issued for within the country.
Issue of pay-Order:
To issue a ‘Pay-Order’ the party should maintain and A/C. with the bank. The bank also allows special customers without A/C for Pay-Order in special circumstances. The main feature of pay-Order is that in where (That is in which branch) the P.O. is issued the party should encash the money form the same branch.
Table: charges of issuing pay order:
| Amount up to (Tk.) | Charge rate (Tk.) | VAT(Tk) |
| 1,00,000 | 25 | 4 |
| 5,00,000 | 60 | 9 |
| Above 5,00,000 | 75 | 11 |
The procedure for selling P.O. is as follows: –
- Purchaser must be an account holder of DBL Agrabad Branch.
- Depositing money with P.O. application form.
- Giving necessary entry in the bills payable (PO) register.
- Payees name, date, P.O. no. Etc.
- Preparing instrument.
- After it has been scrutinized & approval by higher authority, the instrument is delivered to customer. Signature of customer is taken in the counterpart.
Practice and operation of pay order:
Type of P.O.:
Account payee only : only can encash it by depositing it in his Account.
Blank crossed : Any one can encash it by depositing in their account.
Cash payment : Identification regarding payee.
Settlement of a P.O.
When P.O. submitted by collecting bank through clearinghouse, the issuing bank gives payment.
Thus bank’s liability is settled by debiting bills payable. But before giving payment it should be examined whether endorsement was given by the collecting bank or not. If not hen the instrument is dishonored marking ‘Endorsement required’.
Collection of PO:
A customer of HBL who is the payee of a P.O. Will deposits it for collection. The instrument is given to the clearing that will place it to the issuing bank in the clearing house. Before placement, HBL as a collection bank gives necessary endorsement.
¨ Telegraphic Transfer (T.T)
This is the most usable instrument in remittance section. In local office, T.T. Is generally done by telex, telephone is also used necessary.
Issue of T.T:
To issue a T.T the party should maintain an A/C with that issuing Bank.
Then….
- The customer is asked to complete an application that is also treated as credit voucher for head office account (Branch concern)
- Telegram charges are also recovered from the customer and are credited to income account telegram charges covered a credit voucher is prepared for the customer.
- Text of telegram is written and handed over.
- Then the massage is typed on the from.
- The original telegram & confirmation is sent to the dispatch departmet.
- IBCA is prepared in duplicated. A Separated register is maintained for T.T. Issue.
Telegraphic transfer is one of the fastest means of transferring money form one branch to another or from one place to another. The TT issuing bank instrument is given for T.T Both parties should have account, as money is transferred.
Outgoing T.T.-Its Procedure:
- Application by customer along with money given.
- In receipt of money a cost memo is given to the customer containing TT serial number. The customer informs this number to the awaiting party in the other branch.
- Tested fax message is prepared, where TT serial and the of the concern party to whom the money will be credited is mentioned.
- Activity report is received form the telex department confirming transmission of message.
Incoming TT- Practice:
After receiving the fax message it is sent for test agree.
TT serial number is scrutinized in the “TT in -concern branch” register.
Payment of TT:
The payment of TT requires a lot of paper works. Vouchers are made. At first H.O. concern bank is debited with TT payable credited. Then the TT payable is debited with party’s A/C credited. The receiving party can also take the cash after his A/C is credited. For the payment of TT caution must be taken because various fraud and forgery. So test no. is required for security.
¨ Clearing
Clearing is one of the most important functions of general banking. Mainly clearing is an arrangement held in Bangladesh bank where daily representative of the member bank gather to clear their cheques and instruments. The bank receives many such instruments during the from the A/C holders. May of these instruments are draw payable at other banks.
When the bill is within the range of the clearinghouse it is sent for collection through clearing section. As far as safety is concerned customers get crossed cheque for the transaction crossed check can’t be encashed form the counter, rather it has to be collected through banking channel i.e., clearing. If a client of HBL received a check of another bank which is located within the clearing range and deposit the instrument in his account at HBL then HBL will collect the money through clearing house. After received the check HBL will credit client account. However, the amount is credited in the customer A/C but he will no get the money until the check is honored.
Procedures for clearing:
- Received seal is stamped on the cheque.
- Crossing of the cheques are don.
- “Payee’s A/C Credited” endorsement is given.
- Entries are given in the Outward clearing Register.
- Clearing seal is given.
- Cheques are sorted bank wise and entries are given to the computer (NIASH2)
- Entries age given in the clearing House Register before dispatching to the clearing house.
After that, a debit voucher is prepared.
Instruments of other branches:
However, the principal branch clears its checks as well as the checks of other branches because, no other branch is allowed to represent directly. The other branches send the instruments along with IBDA principal Branch acts as an agent in this case.
Dishonor of Cheuqe:
If the cheque is dishonored, HBL sends a memorandum (cheque return memo) to the customer stating the reason.
¨ Outward clearing:
Outward clearing refers to the instruments drawn on other banks and deposited in HBL for collection. The following steps are taken for outward clearing…
¨ The duly signed instruments are received.
¨ The instruments are checked for any kind of discrepancy.
¨ “Received for Clearing” seal is stamped on the counterfoil of the deposit slip.
¨ Instrument is stapled with Deposit Slip.
¨ Special crossing in favor of “Habib Bank Ltd” is given on the instrument there of.
¨ Entry is given in NIKASH.
¨ “Payee’s A/C Credited” endorsement is given.
¨ The instruments are sorted bank wise as well as branch-wise.
¨ Entries are given in the Clearing House Register before dispatching to the clearinghouse.
¨ All the instruments are sent to the First Clearing House to deliver them to the respective banks.
Function in the Clearing House:
- The clearinghouse is an assembly of the locally operating scheduled banks for exchange of checks, drafts, and other demand instruments drawn on each other and received form their respective customers for collection.
- The house meets at the appointed hour on all working days under the chairmanship of the central bank. The clearing house ists twice ina working day.
- The Member submits the claimable checks in the respective desks of the banks and vice-versa.
- Consequently, the debit and credit entries are given.
- At the end, the debit summation and the credit summation are calculated. Then the banks clear the balances through the check of Bangladesh Bank.
- The dishonored checks are sorted and returned with return memo.
- If the instruments are dishonored then they are sorted again and sent back to the returning house along with their return memo.
- Later on all the instruments of HBL which were claimed by other banks are sorted and delivered to respective branches.
- If the instruments are honored the treatment is:
¨ Inward clearing:
Inward clearing refers the instruments drawn on the Agrabad branch, which are received from other banks in the clearinghouse by the representative of other banks. The followings steps are taken for inward clearing………..
- The instruments drawn on the bank, which are received form other banks through clearing house.
- The amounts of number of instruments are entered in the house form the main schedule of respective banks.
- The instruments with schedule are arranged branch wise.
- The instruments send to branches concerned for clearance and IBCA’s are collected form them for honored cheque.
- The instruments are sent to the respective departments and the schedules are filled.
- These sorts of instruments are cleared form the second house of the central bank.
¨ Collection:
When the bills are supposed to be drawn on any bank, which is out of range of clearing house of Bangladesh bank this instrument are sent for collection not clearing. These bills are of two types. They are inward bill for collection and outward bills for collection. We can see a brief scenario about these two types of bill as below
¨ Inward bills for collection:
When instruments received form other branches or other banks, they are treatment as inward bills for collection. In practices instruments of other banks or branches are cleared through clearinghouse. For those instruments form other branches of and other banks outside clearinghouse come under the bill collection procedure.
When the OBC is received form the other bank’s branches, which are treated as outward bills for collection. This collection procedure occurs in two different situations.
FOREIGN TRADE
In
HABIB BANK LTD.
Introduction:
Foreign trade can be easily defined as a business activity, which transcends national boundaries. These may be between parties or government ones. Trades among nations are a common occurrence and normally benefit both the exporter and importer. In many countries, international trade accounts for more than 20% of their national incomes.
Foreign trade can usually be justified on the principle of comparative advantage. According to this economic principle, it is economical profitable for a country to specialize in the production of that commodity in which the producer country has the greater comparative advantage and to allow the other country to produce that commodity in which it has the lesser comparative advantage. It includes the spectrum of goods, services, investment, technology transfer etc.
This trade among various countries causes for close linkage between the parties dealing in trade. The bank which provides such transactions is referred to as rendering international banking operations. International trade demands a flow of goods from seller to buyer and of payment from buyer to seller. And this flow of goods and payment are done through letter of credit (L/C).
Foreign Exchange:
As more than one currency are involved in foreign trade, it gives rise to exchange of currencies which is known as foreign exchange. The term “Foreign Exchange” has three principal meanings Firstly it is a term used referring to the currencies of the other countries in terms of any single one currency. To a Bangladeshi, Dollar, Pound sterling etc. are foreign currencies and as such foreign exchange. Secondly, the term also commonly refer to some interments used in international trade, such as bill of exchange, Drafts, Travel cheque and other means of international remittance thirdly, the terms foreign exchange is also quite of ten referred to the balance in foreign currencies held by a country.
In terms of section 2(d) of the foreign exchange regulations 1947, as adopted in Bangladesh, Foreign Exchange means foreign currency and includes any instrument drawn, accepted made or issued under clause (13) of article 16 of the Bangladesh Bank order, 1972, all the deposits, credits and balances payable in any foreign currency and draft cheque, letter of credit and bill of exchange expressed or drawn in Bangladesh currency but payable in any foreign country.
In exercise of the power conferred by section 3 of the foreign exchange regulation, 1947, Bangladesh Bank issues license to schedule bank to deal with exchange. These banks are known an Authorized Dealers. Licensees are also issued by Bangladesh Bank to persons or firms to exchange foreign currency instruments such as T.C, currency notes and coins. They are known as Authorized money changers.
Functions of Foreign Exchange Department:
Exports:
- Pre-shipment advances.
- Purchase of foreign bills.
- Negotiating of foreign bills.
- Export guarantees.
- Advising/Confirming letters – letter of credit.
- Advance for deferred payments exports.
- Advance against bills for collection.
Imports:
Opening of letter of credit (L/C)
Advance bills.
Bills for collection.
Import loan and guarantees.
Remittances:
- Issue of DD, MT, TT etc.
- Payment of DD, MT, TT etc.
- Issue and enhancement of traveler’s cheque.
- Sale and enhancement of foreign currency notes.
- Non-resident account
FOREIGN TRADE
THREE BROAD CATEGORY
- International Trade Business
- International Remittance
- Foreign Currency Dealings
REGULATORY FRAMEWORK
- Domestic
- International
DOMESTIC
- Foreign Exchange Regulatory Act 1997
- Export Import Act 1950
- Guide Line for Foreign Exchange Transaction
- Foreign Exchange Circular by Bangladesh bank
- Regulation of Ministry of Commerce
INTERNATIONAL
- UCPDC-Uniform customs & practices for documentary credit
- ICC Publications
- URC-Uniform Rules for Collection
- URR-Uniform Rules for reimbursement
- INCOTERMS
MODE OF PAYMENTS IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE
- Cash in advance
- Open Account
- Collection Method
- Documentary Credit
COLLECTION METHOD
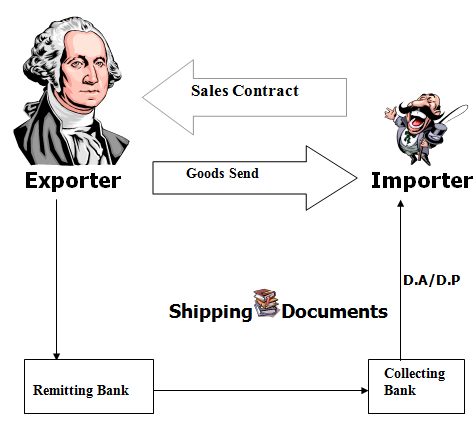
Documentary Credit
- Letter Of Credit – Undertaking of the bank to the exporter on behalf of importer for payment certain amount of money if he fulfills certain terms and conditions.
- Documents – Papers that support the terms & condition of the letter of credit.
DOCUMENTARY CREDIT
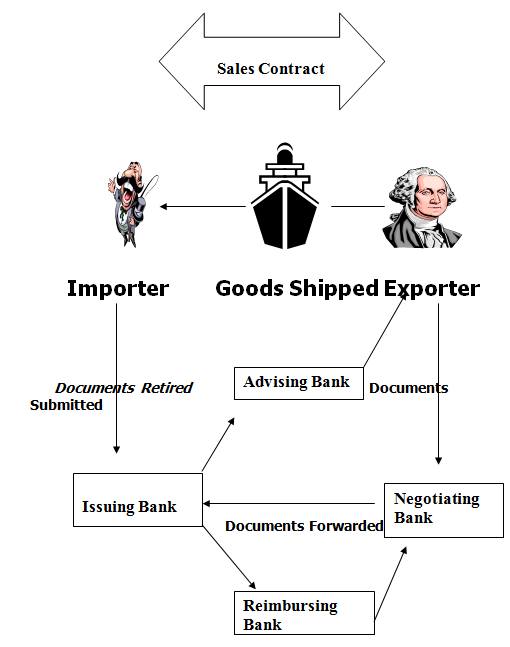
EXCHANGE RATE
- Price of one currency in terms of other currency.
- 1 US Dollar = Tk. 60.00
EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM
- Fixed
- Floating
EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM: BUYING
- TT Clean
- TT OD & Doc
- OD Sight
FLOATING EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM
- INDEPENDENT FLOATING
-Determine by supply and demand of the market
- MANAGED FLOATING
– Central bank will intervene if exchange rate becomes unstable.
– Managing by supplying dollar in the market.
– Managing by reducing the supply of taka in the market.
- PEGGING
– Exchange rate of one currency is tagged/pegged with another
Currency.
– With single currency or basket.
EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM: SELLING
- TT & OD
- BC Selling
TRAVELERS CHEQUE
- What you need to buy TC?
-Valid Passport
-Valid Air Ticket
-Visa
TRAVELERS CHEQUE
- How much can you get?
-SAARC Countries
- Maximum $1000(for air) $500(for road)
-Other Countries
- Maximum $3000
- How much for a year?
- How much for a minor?
- What about cash?
The Most commonly used documents in Foreign Exchange:
- Documentary Letter of Credit.
- Bill of exchange.
- Bill of Lading.
- Commercial Invoice.
- Certificate of origin of goods.
- Inspection certificate.
- Packing List.
- Insurance Policy.
- Proforma Invoice / Indent.
- Master receipt.
- GSP Certificate.
Documentary Credit:
In simple terms a documentary credit is a conditional bank undertaking a payment. Expressed more fully, it is a written undertaking by a bank (issuing bank) given to seller (beneficiary) at the request, and in accordance with the instructions of the buyer (applicant) to effect payment (that is, by making a payment, or accepting or negotiating bill of exchange) up to a stated sum of money, with in a prescribed time limit and against stipulated documents. The customary clauses contain in a L/C are the followings:
- A clause authorizing the beneficiary to draw bills of exchange up to certain on the opener.
- List of shipping documents, which are to accompany the bills.
- Description of the goods to be shipped.
- An undertaking by the opening bank that bills drawn in accordance with the conditions will be dully honored.
- Instructs to the negotiating banks for obtaining reimbursement of payments under the credit.
Parties to a Letter of credit (L/C):
The parties to a Letter of Credit are:
Importer / Buyer.
Opening Bank/Issuing Bank.
Exporter/Seller/Beneficiary.
Advising Bank/Notifying Bank.
Negotiating Bank.
Confirming Bank.
Paying / Reimbursing Bank.
Bill of Lading:
A bill of leading is a document that is usually stipulated in a credit when the goods are dispatched by sea. It is evidence of a contract of carriage, is a receipt for the goods, and is a document of title to the goods. It also constituted a document that is, or may be, needed to support an insurance claim.
The Details on the bill of Leading should include:
- A description of the goods in general terms not inconsistent with in the credit.
- Identify marks and numbers, if any.
- The name of the carrying vessel.
- Evidence that the goods have been loaded on board.
- The ports of shipment and discharge.
- The names of shipper, consignee, and name and address of the notifying party
- Whether freight has been [paid or is payable at destination.
- The number of original bills of lading issued.
- The date of issuance.
A bill of lading specifically states that goods are loaded for ultimate destination specifically mentioned in the credit.
Commercial Invoice:
A Commercial Document is the accounting document by which the sellers change the goods to the buyer. A commercial invoice normally includes the following information:
Date.
Name and address of the buyer and seller.
Order of contract number, quantity and description of the goods, unit price and the total price.
Weight of the goods, number of the package, shipping marks and numbers.
Terms of delivery and payment.
Shipment details.
Certificate of Origin:
A certificate of origin is a signed statement providing evidence of the origin of the goods.
Inspection Certificate:
This is usually issued by an independent inspection company located in the exporting country certifying or describing the quality, specification or other aspects of the goods, as called for in the contract and the L/C. the inspection company is usually nominated by the buyer who also indicates the types of inspection he wishes the company to undertake.
Insurance Certificate:
The Insurance Certificate documents must –
- Be that specified in the credit.
- Cover the risks specified in the credit.
- Be consistent with the other documents in its identification of the voyage and description of the goods.
- Unless otherwise specified in the credit.
- Be a document issued and / or signed by an insurance company or its agent, or by underwriters.
- Be dated on or before the date of the date of shipment as evidenced by the shipping documents.
- Be for an amount at least equal to the CIF value of the goods and in the currency of credit.
Import:
Importation is foreign goods and services purchased by customer, firms and Governments in Bangladesh.
An importer must have import registration certificate (IRC) given by chief controller of import and exports (CCI & E) to import any thing from other country. To obtain import registration certificate (IRC) the following certificates are required:
Trade License.
Income Tax clearance certificate.
Nationality certificate.
Banks solvency certificate.
Asset certificate.
Registration partnership deed (if any).
Memorandum and Article of association.
Certificate of incorporation (if any)
Rent receipt of the business premises.
Import Procedure:
To import through United Commercial Bank Limited (UCBL), a customer/client requires –
- Bank Account.
- Import registration certificate.
- Tax paying identification number.
- Proforma Invoice/Indent.
- Membership Certificate.
- L/C application form duly attested.
- One set of IMP Form.
- Insurance Cover Note with money receipt.
- Others.
Some More Parts-
Report on General Banking Operations in Habib Bank Limited (Part-1)
Report on General Banking Operations in Habib Bank Limited (Part-2)
Report on General Banking Operations in Habib Bank Limited (Part-3)