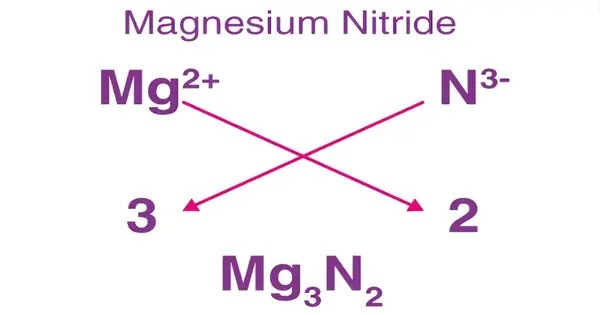
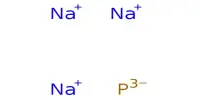Magnesium nitride, which possesses the chemical formula Mg3N2, is an inorganic compound of magnesium and nitrogen. It’s formed when magnesium (Mg) reacts with nitrogen gas (N₂). At room temperature and pressure it is a greenish yellow powder. It’s an interesting material with uses in both industrial and research settings.
Preparation
By passing dry nitrogen over heated magnesium at 800 °C:
3 Mg + N2 → Mg3N2 or ammonia at 700 °C:
3 Mg + 2 NH3 → Mg3N2 + 3 H2
Magnesium nitride is typically formed by burning magnesium in nitrogen. It can also form as a byproduct when magnesium burns in air (due to the nitrogen content of air).
Reactivity
Hydrolyzes in water to form magnesium hydroxide and ammonia:
𝑀𝑔3𝑁2+6𝐻2𝑂 → 3𝑀𝑔(𝑂𝐻)2+2𝑁𝐻3
Properties
- Chemical formula: Mg3N2
- Molar mass: 100.9494 g/mol
- Appearance: greenish yellow powder
- Density: 2.712 g/cm3
- Melting point: approx. 1500°C
Occurrences
Naturally Occurring:
Magnesium nitride does not occur naturally in significant quantities due to its high reactivity with moisture and oxygen.
Synthetically Produced:
Formed by burning magnesium in a nitrogen atmosphere:
3Mg+N2 → Mg3N2
Commonly made in labs or industry via high-temperature reactions.
Uses in Industry and Research
- As a nitrogen source for making nitrides of other metals.
- In solid-state chemistry and ceramic production.
- Sometimes used to produce high-purity ammonia.
- Explored for battery and semiconductor applications.