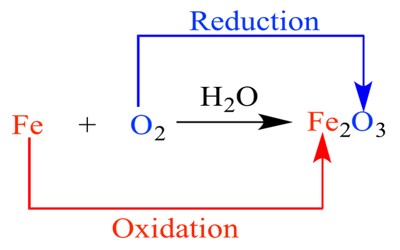
Oxidation is any chemical reaction that involves the moving of electrons. It is the process or result of oxidizing or being oxidized. Specifically, it means the substance that gives away electrons is oxidized. It occurs when an atom, molecule, or ion loses one or more electrons in a chemical reaction.
When oxidation occurs, the oxidation state of the chemical species increases. When iron reacts with oxygen it forms a chemical called rust because it has been oxidized (the iron has lost some electrons) and the oxygen has been reduced (the oxygen has gained some electrons).
Formula of rusting is: 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 xH2O→Fe2O3.x H2O
Oxidation is the opposite of reduction. The reduction in the process via which an atom needs electrons to another. A reduction-reaction always comes together with an oxidation-reaction. Oxidation and reduction together are called redox (reduction and oxidation). Oxygen does not have to be present in a reaction for it to be a redox-reaction.
Oxidation is the loss of electrons. It is the loss of electrons during a reaction by a molecule, atom or ion. It is also the loss of hydrogen. In terms of oxygen transfer, oxidation may be defined as the chemical process in which a substance gains oxygen or loses electrons and hydrogen. Sometimes it is helpful, and sometimes it is very destructive.
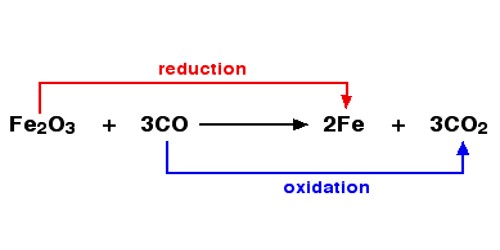
When one of the reactants is oxygen, then oxidation is the gain of oxygen. The reduction is a loss of oxygen. For example:
- Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
Both reduction and oxidation go on at the same time which is a redox-reaction. The loss of hydrogen atoms and the gain of oxygen atoms is known as oxidation. The gain of hydrogen atoms and the loss of oxygen atoms is known as reduction. Oxidation is the gain of oxygen atoms and reduction is the gain of hydrogen atoms.