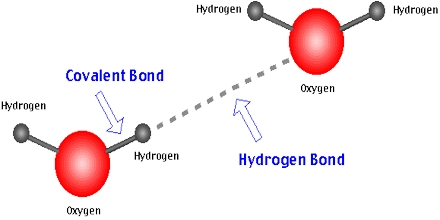
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is liable for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) when compared to the other group 16 hydrides which may have no hydrogen bonds. A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that develops when a hydrogen (H) atom bound into a highly electronegative atom for example nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or perhaps fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby hugely electronegative atom.
Hydrogen Bond