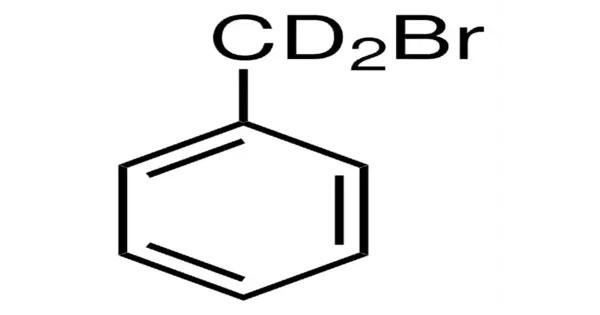
Benzyl bromide is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Br. The molecule consists of a benzene ring substituted with a bromomethyl group. It is a relatively reactive compound due to the presence of the electrophilic bromine atom attached to the benzyl group. It is a colorless liquid with lachrymatory properties. The compound is a reagent for introducing benzyl groups.
It is used in reactions such as nucleophilic substitution and alkylation of aromatic compounds. It is toxic if inhaled or ingested and can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. Proper precautions should be taken when handling it.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C7H7Br
- Molar mass: 171.037 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Odor: Sharp and pungent
- Density: 1.438 g/cm3
- Melting point: −3.9 °C (25.0 °F; 269.2 K)
- Boiling point: 201 °C (394 °F; 474 K)
- Solubility: organic solvents
- Refractive index (nD): 1.5752
Occurrences
Benzyl bromide is primarily synthetic and does not occur naturally in significant quantities. It is produced commercially by bromination of toluene (C₆H₅CH₃), which involves replacing one of the methyl hydrogen atoms with a bromine atom. The process typically takes place in the presence of bromine and light or in a solvent under controlled conditions.
- Chemical Synthesis: It is widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of benzyl derivatives (amines, alcohols, esters).
- Pharmaceuticals: It is used to create benzylated compounds that serve as active ingredients in some pharmaceutical formulations.
- Agriculture: Some pesticides and herbicides contain benzyl bromide as a precursor.
- Polymer Chemistry: It can be used in the preparation of certain polymers and resins.
- Laboratory Reactions: It is employed in nucleophilic substitution reactions to introduce the benzyl group in organic compounds. It’s also used in the synthesis of benzylating agents.
Applications
Benzyl bromide is used in organic synthesis for the introduction of the benzyl groups when the less expensive benzyl chloride is insufficiently reactive. Benzylations are often achieved in the presence of catalytic amounts of sodium iodide, which generates the more reactive benzyl iodide in situ. In some cases, benzyl serves as protecting group for alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Safety
Benzyl bromide is a strong lachrymator and is also intensely irritating to skin and mucous membranes. Because of these properties, it has been used in chemical warfare, both in combat and in training due to its irritating yet non-lethal nature.