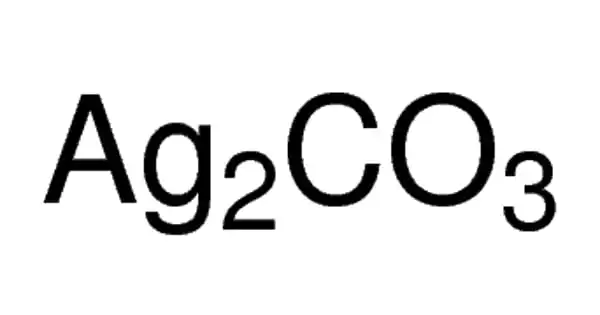Zinc Nitrate (Zn(NO3)2) is a colorless crystalline solid; it is highly deliquescent and is typically encountered as a hexahydrate Zn(NO3)2•6H2O. It is soluble in both water and alcohol. Noncombustible, but accelerates the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided, an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires involving this material. It is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of other chemicals, in medicine, and in dyes.
It is produced by dissolving zinc in nitric acid. The reaction is concentration-dependent and forms ammonium nitrate. The reaction is given below:
Zn + 2 HNO3 (diluted) → Zn(NO3)2 + H2
4 Zn + 10 HNO3 (concentrated) → 4 Zn(NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + 3 H2O
It undergoes thermal decomposition on heating and forms zinc oxide, oxygen, and nitrogen dioxide.
2 Zn(NO3)2 → 2 ZnO + 4 NO2 + O2
Zinc nitrate is a dangerous fire and explosion hazard. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided, an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion.
Zinc nitrate has no large scale application but is used on a laboratory scale for the synthesis of coordination polymers. Its controlled decomposition to zinc oxide has also been used for the generation of various ZnO based structures, including nanowires. It can be used as a mordant in dyeing.
Some Uses of Zinc nitrate –
- Zinc nitrate is used as a synthesis of coordination polymers.
- Used in dyeing as a mordant.
- Used as a catalyst in resin production.
- Used as a strong oxidizing agent.
- Used in liquid fertilizers.
- Used as a latex coagulant.
- Used in the manufacturing of medicines.
Inhaling dust causes irritation in the throat and nose. Swallowing Zinc dinitrate can lead to corrosion of the alimentary tract. Contact with the skin results in irritation and can cause rashes. When heated it may liberate toxic oxides of nitrogen. When it comes in contact with combustible material it can increase the fire intensity.
Zinc nitrate is an indirect food additive for use only as a component of adhesives. The substance is very toxic to aquatic organisms. The substance may cause long-term effects in the aquatic environment. It is strongly advised not to let the chemical enter into the environment.
Aluminum and zinc do not react with concentrated nitric acid due to the formation of a dense, hard to dissolve the oxidation layer due to a process is known as passive oxidation. This protects the metal against further reaction and corrosion. Nevertheless, zinc does react with dilute nitric acid.
Information Sources: