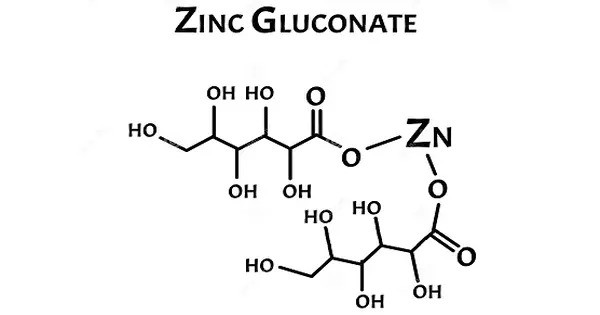
Zinc gluconate is the zinc salt of gluconic acid. It is an ionic compound consisting of two anions of gluconate for each zinc(II) cation. Zinc gluconate is a popular form for the delivery of zinc as a dietary supplement providing 14.35% elemental zinc by weight. It is commonly used as a dietary supplement to provide zinc, an essential mineral that plays an important role in various bodily functions. Zinc is vital for the immune system, wound healing, DNA synthesis, cell division, and growth.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C12H22O14Zn
- Molar mass: 455.685 g/mol
- Melting point: 172 to 175 °C (342 to 347 °F; 445 to 448 K)
Gluconic acid is found naturally, and is industrially made by the fermentation of glucose, typically by Aspergillus niger, but also by other fungi, e.g. Penicillium, or by bacteria, e.g. Acetobacter, Pseudomonas and Gluconobacter. In its pure form, it is a white to off-white powder. It can also be made by electrolytic oxidation, although this is a more expensive process. The advantages are a lower microbiological profile, and a more complete reaction, yielding a product with a longer shelf life.
Stability
Zinc gluconate is relatively stable under normal conditions but can be sensitive to light and moisture. As a supplement, it is often found in tablet or lozenge forms, sometimes flavored to mask the taste.
Natural Occurrence
Zinc itself is naturally occurring in many foods, including meat, shellfish, dairy, seeds, and nuts. Zinc gluconate, however, does not occur naturally in its pure form. It is synthesized in laboratories for pharmaceutical and supplemental use.
Uses
- Immune Support: Zinc is known for its role in supporting immune function, and zinc gluconate is often taken to prevent or reduce the duration of colds. It is frequently used in lozenges for this purpose.
- Skin Health: Zinc plays a role in maintaining skin integrity, so zinc gluconate is sometimes used in the treatment of acne or other skin conditions.
- Antioxidant Properties: Zinc is an antioxidant, helping to neutralize free radicals and protect cells from damage.
- Digestive Health: Zinc is involved in the digestion process, and it supports the body’s ability to metabolize food.
- Deficiency Treatment: Zinc deficiency can lead to issues such as weakened immunity, stunted growth, hair loss, and poor wound healing. Zinc gluconate can be used to correct deficiencies.