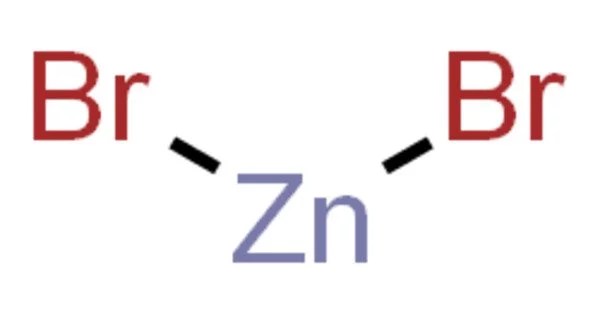
Zinc bromide (ZnBr2) is a chemical compound with the formula ZnBr2. It is a colorless salt with many properties in common with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), including high solubility in water, which forms acidic solutions, and good solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and reacts with water to form the dihydrate ZnBr2•2H2O.
It is used as a Lewis acid in organic chemistry. It functions as the electrolyte in a zinc bromide battery. Solutions containing zinc bromide are used in oil and natural gas wells to displacing drilling mud when transitioning from the drilling phase to the completion phase or during well workover operations.
Properties
Zinc bromide is an odorless white crystalline solid or white hygroscopic powder. It is mainly used in the oil industry, electrolysis, catalysis, the electrical industry, and metalworking companies. It is an environmentally hazardous substance and has a corrosive effect.
- Chemical formula: ZnBr2
- Molar mass: 225.198 g/mol
- Appearance: white crystalline powder hygroscopic
- Density: 4.20 g/cm3 (20 °C); 4.22 g/cm3 (25 °C)
- Melting point: 394 °C (741 °F; 667 K)
- Boiling point: 697 °C (1,287 °F; 970 K)
- Solubility in water: 388 g/100 mL (0 °C); 675 g/100 mL (100 °C, for the anhydrous material)
- Solubility: very soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, tetrahydrofuran

Production
Zinc bromide solutions can be used as a transparent radiation shield. The density of two glass panes filled with a strong aqueous solution of zinc bromide is very high, and it can be used as a window on a hot cell. This type of window has an advantage over lead glass in that it does not darken as a result of radiation exposure. Radiation causes all glass to darken gradually over time, but this is especially true in a hot cell, where exceptional levels of radiation are present. The benefit of using an aqueous salt solution is that any radiation damage will last less than a millisecond, allowing the shield to self-repair.
ZnBr2 · 2H2O is prepared by treating zinc oxide or zinc metal with hydrobromic acid.
ZnO + 2 HBr + H2O → ZnBr2·2H2O
Zn + 2 HBr → ZnBr2 + H2
The anhydrous material can be produced by dehydration of the dihydrate with hot CO2 or by reaction of zinc metal and bromine. Sublimation in a stream of hydrogen bromide also gives the anhydrous derivative.
Uses
Zinc bromide is used in the following applications:
- In organic chemistry as a Lewis acid.
- It is the electrolyte in the zinc bromide battery.
Solutions containing zinc bromide are used in oil and natural gas wells to displace drilling mud when transitioning from the drilling phase to the completion phase or during well workover operations. The fluid’s weight of 20 pounds per gallon is due to the extremely dense brine solution, which makes it particularly useful in holding back flammable oil and gas particles in high pressure wells. The high acidity and osmolarity, on the other hand, cause corrosion and handling issues. Because the fluid is so dehydrating, crews must wear slicker suits and rubber boots.
Zinc bromide solutions can be used as a transparent radiation shield. To be used as a window on a hot cell, the space between two glass panes is filled with a strong aqueous solution of zinc bromide with a very high density. This type of window has an advantage over lead glass in that it does not darken as a result of radiation exposure. Radiation causes all glass to darken gradually over time, but this is especially true in a hot cell, where exceptional levels of radiation are present. The benefit of using an aqueous salt solution is that any radiation damage will last less than a millisecond, allowing the shield to self-repair.
Safety
Safety considerations are similar to those for zinc chloride, for which the toxic dose for humans is 3–5 g.