Triphenyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OC6H5)3. It is a colourless viscous liquid. It consists of a phosphorous atom bonded to three phenyl groups (C₆H₅) and an oxygen atom. This compound is commonly used as a stabilizer, plasticizer, and in various chemical syntheses.
Preparation
Triphenylphosphite is prepared from phosphorus trichloride and phenol in the presence of a catalytic amount of base:
PCl3 + 3 HOC6H5 → P(OC6H5)3 + 3 HCl
Reactions
Triphenylphosphite is a precursor to trimethylphosphine, it serves as a source of P3+ that is less electrophilic than phosphorus trichloride:
(C6H5O)3P + 3 CH3MgBr → P(CH3)3 + 3 “MgBrOC6H5”
Triphenylphosphite is quaternized by methyl iodide:
(C6H5O)3P + CH3I → [CH3(C6H5O)3P]+I−
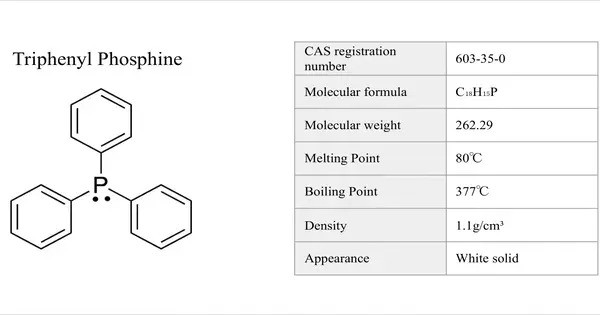
Properties
- Chemical formula: C18H15O3P
- Molar mass: 310.28 g/mol
- Appearance: colourless liquid
- Density: 1.184 g/mL
- Melting point: 22 to 24 °C (72 to 75 °F; 295 to 297 K)
- Boiling point: 360 °C (680 °F; 633 K)
- Solubility in water: low
- Solubility: organic solvents
Chemical Behavior
- Hydrolysis: When exposed to moisture or water, triphenyl phosphite undergoes hydrolysis, producing phosphoric acid and phenol.
- Reactions with Halogens: It reacts with halogens to form corresponding halogenated derivatives, which are important intermediates in organic synthesis.
- Stabilizing Agent: It can act as a stabilizer in polymers, particularly in the presence of metal ions or as a plasticizer in certain resins.
- Ligand Chemistry: Due to its ability to coordinate with metal centers, triphenyl phosphite is used in catalysis and other metal-based reactions.
Occurrences
Triphenyl phosphite does not naturally occur in large quantities in nature, as it is primarily synthesized for industrial use. It is usually produced by reacting phenol with phosphorus trichloride (PCl₃). This reaction is a well-known method of preparing triphenyl phosphite:
PCl3+3C6H5OH→(C6H5O)3P+3HClPCl₃ + 3C₆H₅OH → (C₆H₅O)₃P + 3HClPCl3+3C6H5OH→(C6H5O)3P+3HCl
In this reaction, phenol acts as a nucleophile and displaces the chloride ion from phosphorus trichloride, forming the triphenyl phosphite.
Uses
- Plasticizers: Triphenyl Phosphite is often used as a plasticizer in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and other polymers.
- Stabilizer for Polymers: It is used in the stabilization of PVC and other plastics, protecting them from degradation during processing.
- Reagent in Organic Synthesis: TPP can be used in the synthesis of various organic compounds, especially in reactions involving the protection of hydroxyl groups or the modification of other phosphorus-containing compounds.
- Antioxidant: It acts as an antioxidant in certain polymer systems.
- Ligand in Catalysis: TPP can serve as a ligand in various catalytic reactions, particularly in organometallic chemistry.
Safety
- Toxicity: It can be harmful if inhaled, ingested, or if it comes into contact with the skin. It is recommended to handle it with appropriate protective equipment, including gloves and goggles.
- Environmental Impact: Like many organophosphorus compounds, it should be disposed of properly to avoid environmental contamination.