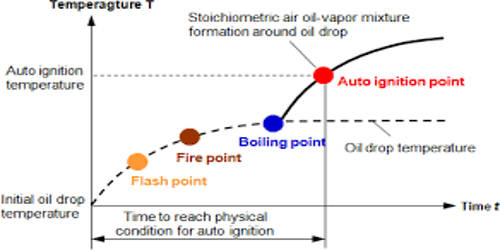
The fire point of a fuel is the lowest temperature at which the vapor of that fuel will continue to burn for at least 5 seconds after ignition by an open flame of standard dimension. It is the lowest temperature at which a volatile combustible substance continues to burn in the air after its vapors have been ignited. It means; the term fire point describes that it is the lowest temperature for a substance to hold the combustion for a small time period after the ignition by an open flame. At the flashpoint, a lower temperature, a substance will ignite briefly, but vapor might not be produced at a rate to sustain the fire. Hence, the flashpoint is the minimum temperature at which the liquid gives off enough vapor to form a combustible mixture with air. Most tables of material properties will only list material flashpoints. Although in general the fire points can be assumed to be about 10 °C higher than the flashpoints, although this is no substitute for testing if the fire point is safety-critical.
Testing of the fire point is done by open cup apparatus. It describes the lowest temperature at which the fuel continues to burn for a short time period after the initiation of the ignition. It is the temperature to which fuel oil must be heated to burn continuously when exposed to an open flame. is the lowest temperature where the vapor of a liquid will initiate and sustain a combustion reaction. The fire point of a hydrocarbon liquid is the higher temperature at which the oil vapors will continue to burn when ignited. In general, the open flashpoint is 50–70°F less than the fire point.
Characteristics:
- The fire point of a flammable liquid is slightly higher than its flashpoint.
- It always larger than flash point and it happens when the surface of sample firing.
- It is usually 10°C more than the flashpoint of a liquid.
- It is the temperature at which vapors of the flammable liquid continue to burn after being ignited even after the source of ignition is removed.
- It is the temperature at which the vapor continues to burn when ignited and after the source of heat has been removed.