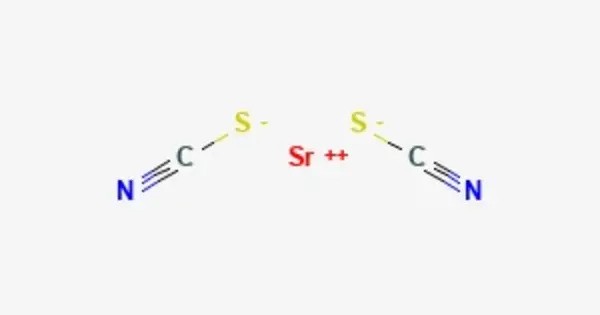
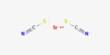
Strontium thiocyanate refers to the salt Sr(SCN)2. It is the thiocyanate salt of the alkaline earth metal strontium, consisting of strontium cations (Sr²⁺) and thiocyanate anions (SCN⁻). It is a colorless solid. It is less common compared to other thiocyanates but has niche applications in research and materials science.
According to X-ray crystallography, it is a coordination polymer. The Sr2+ ions are each coordinated to eight thiocyanate anions in a distorted square antiprismatic molecular geometry where each square face contains two adjacent S atoms and two adjacent N atoms. The motif is reminiscent of the fluorite structure. The same structure is observed for Ca(SCN)2, Ba(SCN)2, and Pb(SCN)2.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C2N2S2Sr
- Molar mass: 203.78 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white solid
- Melting point: 331–379 °C (decomposes at 650 °C)
- Solubility: Soluble in water and polar organic solvents (like ethanol, methanol, and acetone).
- Hygroscopic nature: Tends to absorb moisture from the air, leading to hydrolysis.
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions, but decomposes when strongly heated, releasing toxic gases such as sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides.
Reactivity
- Reacts with acids to form hydrogen thiocyanate (HSCN).
- Can act as a ligand provider in coordination complexes with transition metals.
Preparation
Strontium thiocyanate can be synthesized by:
Neutralization reaction: Sr(OH)2+2HSCN→Sr(SCN)2+2H2O
or
Salt metathesis reaction: SrCl2+2NaSCN→Sr(SCN)2+2NaCl
Applications
- Analytical chemistry: Used as a reagent in certain spectroscopic or precipitation tests.
- Coordination chemistry: Provides thiocyanate ligands to form complexes with transition metals, useful in structural and bonding studies.
- Material science: Investigated for potential roles in polymer modification, catalysis, and ionic conductivity research.
- Research uses: Acts as a source of both Sr²⁺ and SCN⁻ ions in experimental studies.
Safety and Hazards
Toxicity: Both strontium salts and thiocyanates can be harmful if ingested or inhaled.
Health hazards:
- Irritant to skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Thiocyanates may interfere with thyroid function due to competition with iodine uptake.
Decomposition hazards: Heating produces toxic gases (CO, NOx, SO₂, CS₂).
Precautions: Handle with gloves, eye protection, and in a fume hood. Avoid release into the environment.