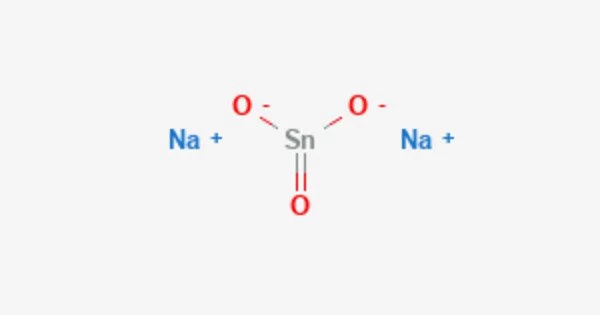
The inorganic compound sodium stannate, formally sodium hexahydroxostannate(IV), has the formula Na2[Sn(OH)6]. It is commonly referred to as sodium meta-stannate or sodium stannate(V). This colorless salt is formed by dissolving metallic tin or tin(IV) oxide in sodium hydroxide and is used as a hydrogen peroxide stabilizer. This compound is composed of sodium ions (Na+) and stannate ions (SnO32-).
Stannates are sometimes represented in older literature as having the simple oxyanion SnO32, in which case this compound is sometimes named sodium stannate-3-water and represented as Na2SnO3•3H2O, a hydrate with three waters of crystallisation. Na2SnO3, the anhydrous form of sodium stannate, is recognized as a separate compound with its own CAS Registry Number, 12058-66-1, and material safety data sheet.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Na2SnO3
- Molecular weight: The molar mass is approximately 214.69 grams per mole.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, and the solubility increases with temperature.
- pH: It solutions are alkaline in nature due to the hydrolysis of the compound in water, which results in the formation of hydroxide ions (OH-).
- Stability: It is relatively stable under normal conditions. However, it can decompose upon heating or in the presence of strong acids or oxidizing agents.
Preparation
Alkali metal stannate compounds are prepared by dissolving elemental tin in a suitable metal hydroxide, in the case of sodium stannate by the reaction:
Sn + 2 NaOH + 4 H2O → Na2[Sn(OH)6] + 2 H2
A similar reaction occurs when tin dioxide is dissolved in base:
SnO2 + 2 NaOH + 2 H2O → Na2[Sn(OH)
The anhydrous form can also be prepared from tin dioxide by roasting with sodium carbonate in a mixed carbon monoxide / carbon dioxide environment:
SnO2 + Na2CO3 → Na2SnO3 + CO2
The anion is a coordination complex that is octahedral in shape, similar to most stannates, such as the hexachlorostannate anion [SnCl6]2−. The Sn—O bond distances average 2.071 Å.
Application
- It is used as a reducing agent and stabilizer in electroplating processes, particularly for the deposition of tin or tin alloys onto metal surfaces. It helps improve the adhesion and appearance of the plated metal.
- It is employed in the textile industry for mercerization, a process that enhances the luster and strength of cotton fibers.
- It is utilized in the production of glass, where it serves as a fining agent. It aids in the removal of small air bubbles and other impurities from molten glass, resulting in a clearer and more homogeneous final product.
- It can act as a catalyst or a precursor for catalysts in certain chemical reactions, including esterification and transesterification processes.
It’s important to note that sodium stannate should be handled with care due to its caustic nature and potential hazards. Proper safety precautions, including wearing protective equipment, should be followed when working with this compound.