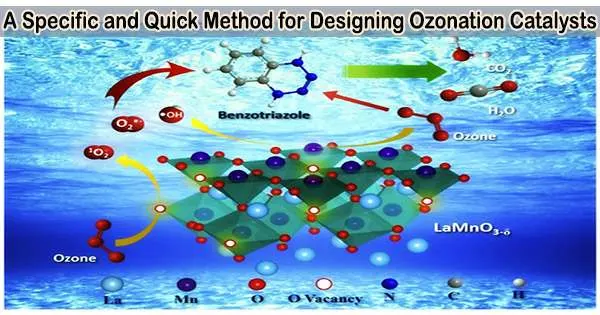
Researchers from the Chinese Research Academy of Environment Sciences recently used machine learning, more specifically the artificial neural network (ANN) model, to forecast catalyst performance based on information gathered from 52 different catalysts. Their findings were published in the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology.
The robustness of the ANN model in foretelling catalyst activity was proved by the model’s good correlation and generalization capabilities. The machine learning model also included fluorescence spectroscopy, which offers useful data on the content and concentration of organics in wastewater. This innovative approach leads to more efficient and effective treatment of refractory organics.
Using the Mn/γ-Al2O3 catalyst as an example, the researchers successfully screened a range of catalyst formulations using fluorescence spectroscopy. They determined the optimal impregnation concentration and time of Mn(NO3)2 for specific wastewater compositions.
The ANN model then generated an optimized formulation for the Mn/γ-Al2O3 catalyst, resulting in improved catalytic performance. The predicted and experimental results for the removal of total organic carbon are very similar, indicating that the improved catalyst is working as intended.
The study also identified the synergistic effect of oxidation radicals (•OH and 1O2) and the Mn/γ-Al2O3 catalyst as the key factors contributing to the improved performance.
Based on the distinct properties of wastewater quality, this novel approach provides a quick and customized option for building ozonation catalysts. Researchers can more effectively adjust catalyst formulation through the use of fluorescence spectroscopy and machine learning, which will improve the treatment of refractory organics in industrial wastewater.
The use of the ANN model in conjunction with fluorescence spectroscopy has the potential to significantly advance the development of catalysts, performance forecasting, and process modeling in sophisticated wastewater systems.
With the help of this strategy, wastewater treatment researchers and practitioners may create more effective and environmentally friendly treatment processes.