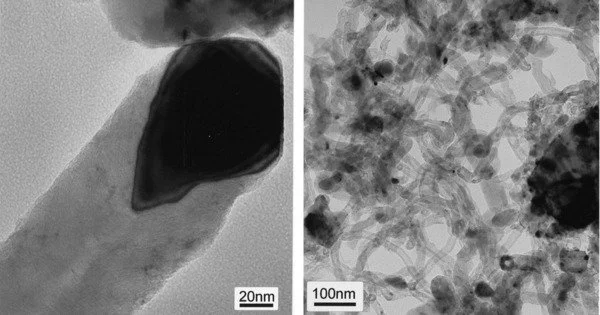
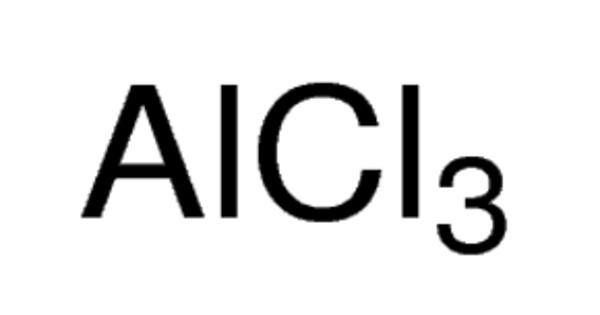Filamentous carbon is a carbon-containing deposit structure that includes numerous carbon allotropes such as carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, and microcoils. It is a form of carbon material with a fibrous or filamentous structure. It is made up of gaseous carbon compounds. These filaments are made up of carbon atoms that have been linked together in various ways to form long, thin structures. It can assume various forms, each with its own set of qualities and applications.
Metal particles are present in all filamentous carbon formations. These are either iron, cobalt, or nickel, or alloys of these metals. Its deposits also have a considerable impact on the synthesis gas methanation. Acetylene is used in a variety of methods for producing filamentous carbon. The filamentous carbon structures are mesoporous and measure on the micrometer scale. The majority of the reactions that generate the structures occur at or above 280 °C (536 °F).
Here are a few common types:
- Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs): Carbon nanotubes are the most well-known form of filamentous carbon. They are hollow cylinders consisting of hexagonally organized carbon atoms. CNTs have high mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity, which makes them useful in a variety of sectors such as nanotechnology, electronics, and materials research.
- Carbon Fibers: Another type of filamentous carbon is carbon fibers. Carbon atoms are used to make thin, flexible filaments. Because of their high strength-to-weight ratio, these fibers are commonly utilized in composite materials for aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment applications.
- Carbon Nanofibers (CNFs): Carbon nanofibers are similar to carbon nanotubes but have a more disordered structure. They can be used in applications like catalysis, energy storage, and reinforcement in composite materials.
- Carbon Whiskers: Carbon whiskers are long, thin filaments of carbon with a high aspect ratio. They’ve been employed in a variety of applications, including material reinforcement, electron emitters in electron microscopy, and high-performance composites.
- Vapor-Grown Carbon Fibers (VGCFs): VGCFs are another type of filamentous carbon that can be synthesized through chemical vapor deposition methods. They have unique properties that make them useful in applications like conductive additives in batteries and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.
Applications
Filamentous carbon has applications such as cleaning up crude oil spills and making strong and lightweight composites. Filamentous carbon has very different thermodynamic properties than graphite, another kind of carbon. However, filamentous carbon is made up of graphite sheets to some extent.
The qualities and applications of filamentous carbon materials vary depending on the structure, length, and diameter of the material. Because of their unique combination of features, including as high strength, electrical conductivity, and thermal stability, researchers continue to investigate novel ways to produce and use these materials in a wide range of technological applications.