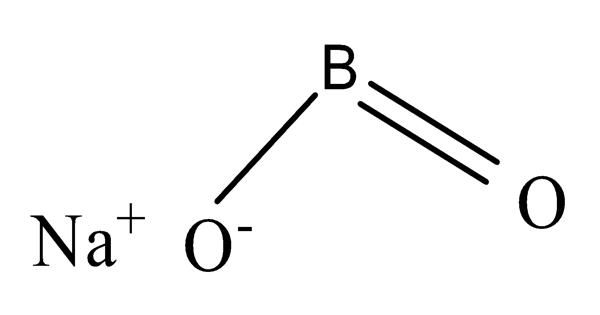
Sodium metaborate is an inorganic sodium salt having metaborate as the counterion. It is a colorless solid chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen with the formula NaBO2. It is an inorganic sodium salt and a member of borate salts. The formula can be written also as Na2O·B2O3 to highlight the relation to the main oxides of sodium and boron.
It also has role in hydrolysis of sodium borohydride to minimize the water utilization. It can also act as a novel alkali in alkali/surfactant/polymer flooding. It is also useful in the thermo-chemical production of sodium borohydride, which is a safe and practical hydrogen storage material for on-board hydrogen production. Sodium metaborate is incorporated in many proprietary water treatment chemicals requiring pH control and corrosion inhibition. They are used for protecting central heating systems and cooling towers against corrosion.
Properties
Sodium metaborate is stable at ordinary temperatures. If exposed to the atmosphere for extended periods, it will pick up carbon dioxide from the air and form sodium carbonate and borax. Sodium metaborate shows little tendency to cake except after prolonged storage or if it becomes severely wetted by rain or substantial water penetration.
- Melting point: 966 °C
- Boiling point: 1434 °C
- Density: 2.464
- Form: white hexagonal crystals.

Preparation
Sodium metaborate is prepared by the fusion of sodium carbonate and boron oxide B2O3 or borax Na2B4O7. Another way to create the compound is by the fusion of borax with sodium hydroxide at 700°C:
B2O3 + 2 NaOH → 2 NaBO2 + 2 H2O
The boiling point of sodium metaborate (1434°C) is lower than that of boron oxide (1860°C) and borax (1575°C) In fact, while the metaborate boils without change of composition, borax gives off a vapor of sodium metaborate with a small excess of sodium oxide Na2O.
The crystalline salt begins to dissolve in its own water at about 90°C (194°F). The anhydrous salt fuses to a clear glass at 966°C (1770°F). Some vaporization occurs above 1230°C (2246°F).
Uses
Sodium metaborate is used as a component of photographic developers and replenishers. Its principal function as a buffering agent is to control the pH within close limits. Sodium metaborate is used in the manufacturing of borosilicate glasses. It is also a component of herbicides and antifreeze products. It is used in the manufacturing of borosilicate glasses. It is also a component of herbicides and antifreeze1. It can also be used as an oil additive with anti-wear properties.
Information Source: