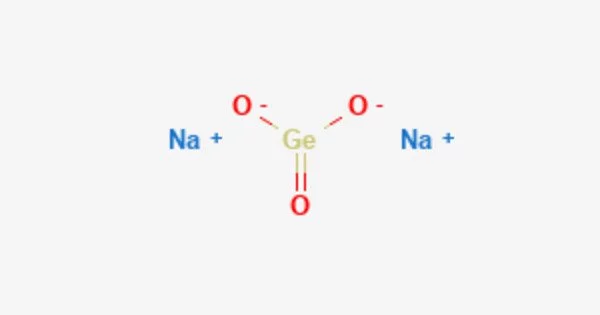
Sodium germanate is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2GeO3. It is a colorless solid. It is an inorganic compound that belongs to the family of germanates, which are salts containing the germanate ion (GeO32-). Sodium germanate is primarily used for the synthesis of other germanium compounds.
Sodium germanate has applications in various fields, including glass manufacturing, catalysts, and solid-state electrolytes in batteries.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Na2GeO3
- Molar mass: 166.62 g/mol
- Appearance: white solid
- Odor: odorless
- Density: 3.31 g/cm3
- Melting point: 1,060 °C (1,940 °F; 1,330 K)
- Solubility in water: 14.4 g/100 mL (0 °C); 23.8 g/100 mL (25 °C)
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, forming an alkaline solution due to the presence of sodium ions.
- Stability: It is stable under normal conditions, but it may decompose when exposed to high temperatures or strong acids.
Preparation and reactions
Sodium germanate can be obtained by reacting sodium hydroxide (NaOH) with germanium dioxide (GeO2). It can be prepared by the fusion of germanium oxide with sodium hydroxide at high temperatures:
2 NaOH + GeO2 → Na2GeO3 + H2O
An intermediate in this reaction is the protonated derivative NaHGeO3, which is a water-soluble salt. It typically exists as a white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and forms alkaline solutions due to the presence of sodium hydroxide. It can also be prepared in an amorphous or glassy form.
Application
Sodium germanate has been studied for various applications, particularly in the field of solid-state ion conductors and glasses. It exhibits interesting ionic conductivity properties, making it potentially useful as an electrolyte in batteries or fuel cells. Its chemical and physical properties make it a subject of research in materials science and solid-state physics.