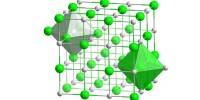
Rubidium fluoride (RbF) is the fluoride salt of rubidium. It is a cubic crystal with a rock-salt structure. Rubidium can be found in the minerals pollucite, carnallite, leucite, and lepidolite. It is extracted commercially from lepidolite as a byproduct of lithium extraction. Rubidium is also found in potassium minerals and brines, which are a commercial source.
It is used as a raw material in the production of rubidium metal and various rubidium salts, as well as in the production of catalyst and high energy density microcells and crystal scintillation counters.
Properties
Rubidium fluoride is a colorless crystal powder with hygroscopic properties. It is a fluoride of minor metal. RbF dissolves in water and hydrofluoric acid but not in ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether, or liquid ammonia. The raw material is rubidium carbonate, rubidium hydroxide, or rubidium metal.
- Compound Formula: FRb
- Molecular Weight: 104.47
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Melting Point: 795 °C
- Boiling Point: 1,408 °C
- Density: 3.557 g/cm3
- Solubility in H2O: N/A

Synthesis
There are several methods for synthesizing rubidium fluoride. One involves reacting rubidium hydroxide with hydrofluoric acid:
RbOH + HF → RbF + H2O
Another method is to neutralize rubidium carbonate with hydrofluoric acid:
Rb2CO3 + 2HF → 2RbF + H2O + CO2
Another possible method is to react rubidium hydroxide with ammonium fluoride:
RbOH + NH4F → RbF + H2O + NH3
The least used method due to the expense of rubidium metal is to react it directly with fluorine gas, as rubidium reacts violently with halogens:
2Rb + F2 → 2RbF
Applications
As a chemical reagent, rubidium fluoride is used. RbF is also used as a raw material in the production of toothpaste. It is used as a raw material in the production of rubidium metal and various rubidium salts, as well as in the production of catalysts and high energy density microcells and crystal scintillation counters.
Outside of research, rubidium is rarely used. It has been used in photocells, to remove traces of oxygen from vacuum tubes, and to create special types of glass. Because it is easily ionized, it was considered for use in ion engines, but it was discovered to be less effective than cesium. It has also been suggested that it be used as a working fluid in vapor turbines and thermoelectric generators.
Health hazards
Rubidium is non-toxic and has no known biological function. However, because it is chemically similar to potassium, we absorb it from food, and the average person has about half a gram stored. Because it is slightly radioactive, it has been used to locate brain tumors because it accumulates in tumors but not in normal tissue.