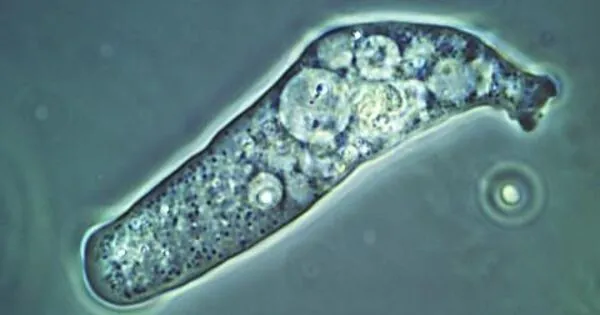
Organotrophs are creatures that derive their energy from the oxidation of organic molecules. It is a type of bacterium that extracts hydrogen or electrons from organic substrates. In microbiology, this word is used to define and describe organisms based on how they obtain electrons for their respiration activities.
Animals and many microbes are both organotrophs and heterotrophs. Organotrophs can be anaerobic or aerobic in nature. In microbiology and ecology, the phrase is frequently used to define a group of organisms depending on their dietary strategy. Organotrophs rely on organic molecules for carbon and energy in their metabolic processes.
There are two main types of organotrophs:
- Chemoorganotrophs: These creatures gain energy by chemically breaking down organic molecules. Many bacteria, fungi, and protozoa are included in this group. Chemoorganotrophs obtain energy from the oxidation of organic materials such as sugars or other organic molecules, which they then use to power their cellular functions.
- Photoorganotrophs: To execute metabolic processes, these organisms mix organic molecules with light energy. A photoorganotroph is a type of bacteria that can use light energy as well as organic substances as a carbon source.
Organotrophs can be further classified based on their specific metabolic processes. For example, some organotrophs are chemotrophs, obtaining energy through chemical reactions, while others may be phototrophs, relying on light energy for their metabolic processes. Heterotrophs are a broader category that includes organotrophs, as they obtain carbon and energy from organic sources.
In summary, organotrophs are creatures that use organic molecules as a source of energy and play an important part in a variety of ecological processes, including the decomposition of organic materials in ecosystems.
Organotrophs are distinguished from lithotrophs, which derive energy from the oxidation of inorganic materials, and autotrophs, which may synthesis their own organic molecules utilizing inorganic chemicals as a carbon source. The dietary and metabolic strategies of organisms are used to categorize them.