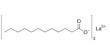
Magnesium ozonide is a compound with the formula MgO3. Much like other ozonides, it is only stable at low temperatures. Unlike other ozonide compounds, magnesium ozonide is white rather than the typical red colour. This compound is quite reactive due to the presence of ozone, which is a strong oxidizing agent.
Magnesium ozonide is usually formed by exposing magnesium to ozone under specific conditions, often in the presence of oxygen. The compound itself can decompose rapidly, releasing ozone, which is unstable and can break down into oxygen (O₂) and reactive oxygen species.
Preparation
Magnesium ozonide can be made by passing a dilute mixture of ozone in liquid nitrogen and over magnesium at -259 °C:
O3 + Mg → MgO3
Magnesium is also known to form bisozonide complexes, containing Mg(O3)2 complexed with argon or carbon monoxide, in an argon matrix.
Properties
- Chemical formula: MgO3
- Molar mass: 72.302 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White solid
- Instability: It is highly unstable and decomposes rapidly, especially at higher temperatures or when exposed to light.
- Decomposition: It decomposes to magnesium oxide (MgO) and oxygen (O₂), releasing ozone in the process.
- Oxidizing Agent: It is a strong oxidizing agent because it contains ozone, which is a reactive molecule.
Occurrence
Magnesium ozonide is not typically found in nature in significant quantities, as it is quite unstable and decomposes under most conditions. It may be synthesized in laboratory settings or formed in specific reactions where ozone interacts with magnesium. For example, it can be generated by exposing magnesium metal to ozone under controlled conditions, though such conditions are not common outside of specialized environments.