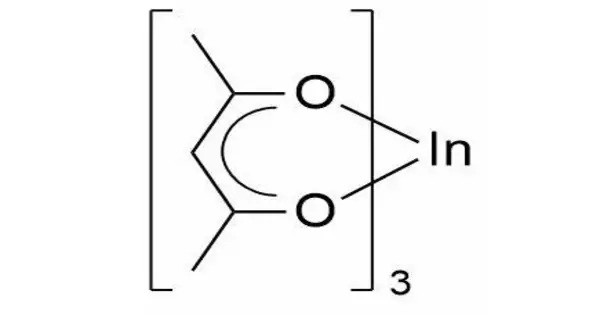
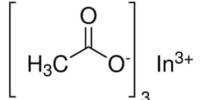
Indium acetylacetonate, also known as In(acac)3, is a compound with formula In(C5H7O2)3. It is a colorless solid. It adopts an octahedral structure. It consists of indium ions coordinated to three acetylacetonate ligands (acac). It can act as a catalyst in organic reactions. It is used in the production of indium oxide films for electronic applications. It serves as a precursor for the synthesis of indium-containing materials.
The compound is typically a solid at room temperature and can be soluble in organic solvents. Safety precautions should be taken when handling it, as with other chemical compounds.
Properties
Indium acetylacetonate features indium ions coordinated to three acetylacetonate ligands. The acetylacetonate acts as a bidentate ligand, coordinating through its oxygen atoms. It typically appears as a solid, often yellowish in color. It is soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, acetone, and toluene but less soluble in water.
- Chemical formula: C15H21InO6
- Molar mass: 412.145 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white
- Density: 1.52 g/cm3
Synthesis
Indium acetylacetonate is not found in nature but is synthesized in laboratories. It is often produced through the reaction of indium salts with acetylacetone.
Uses
Indium acetylacetonate can be used to prepare indium tin oxide thin films with an atmospheric‐pressure chemical vapor deposition method. The resulting thin films are transparent and conductive, with a thickness of about 200 nanometers.
This compound is primarily used in materials science, particularly in the preparation of indium oxide thin films for electronic applications. It is also studied for its potential use in catalysts and as a precursor for indium-containing materials in various chemical reactions.