Gadoxetic acid is a gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent. It is particularly useful for evaluating liver diseases, including liver tumors, cirrhosis, and other hepatic conditions. Its salt, gadoxetate disodium, is marketed as Primovist in Europe and Eovist in the United States by Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals.
Gadoxetic acid is a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA) that helps to improve the visibility of the liver and its blood vessels during MRI scans. It has a relatively short half-life in the bloodstream, which is typical for MRI contrast agents. The elimination from the body happens over several hours.
Properties
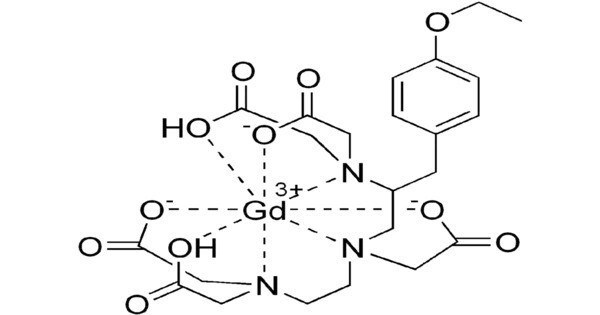
- Chemical Structure: Gadoxetic acid is a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). Its molecular formula is C18H18GdN3O8, and it contains a gadolinium ion (Gd³⁺) that is complexed with organic molecules, which are essential for its imaging properties.
- Magnetic Properties: It contains gadolinium, which has strong paramagnetic properties. This means it can significantly enhance the MRI signal, allowing for better differentiation of tissues and lesions in images.
- Water Solubility: The contrast agent is water-soluble, which allows it to be injected into the body through the bloodstream where it can accumulate in specific tissues, improving imaging of organs, especially the liver.
- Excretion: It is predominantly excreted by the liver, and its clearance from the body happens primarily through the biliary route (via bile). This is beneficial in visualizing liver functions and pathologies.
Here’s how it works:
- Uptake in liver cells: Gadoxetic acid is taken up by hepatocytes (liver cells) in the liver. After injection into the bloodstream, it gets concentrated within the liver tissue, particularly in normal hepatocytes. However, in liver tumors (especially hepatocellular carcinoma), this uptake may be abnormal or absent, which helps in differentiating between normal and pathological tissue.
- Excretion: The agent is partially excreted by the liver and partially by the kidneys. This makes it useful for evaluating both liver function and the presence of any abnormalities.
The main uses of gadoxetic acid include:
- Liver imaging: To assess liver lesions and tumors.
- Liver function assessment: To study the functional status of the liver, especially in cases of chronic liver disease.
- Differentiating between benign and malignant liver lesions: It can help distinguish between different types of liver lesions, including primary liver cancers and metastatic lesions.
Medical uses
It is used to increase the T1 signal intensity while imaging the liver lesions such as benign cysts, hemangioma, and liver cancer. It is excreted into bile by active secretion.
Pharmacokinetics
In those with end-stage renal failure, the clearance rate is only 17% with terminal half-life of 12 times longer than those with normal renal function.
Toxicity
Like other gadolinium-based contrast agents, excessive exposure to gadolinium can potentially be harmful, particularly in patients with impaired kidney function. There have been reports of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF), a rare but serious condition in patients with kidney disease who are exposed to high amounts of gadolinium.