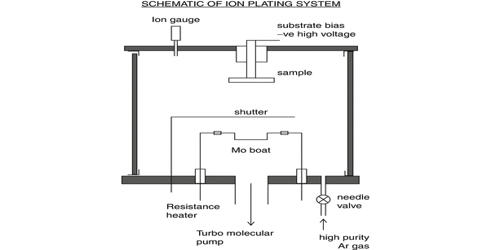
Ion plating (IP) is the method by which substance coatings, typically a compound or metal, are deposited on target surface areas. It is an exciting and new modern technique used for a variety of applications. It is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process that is sometimes called ion-assisted deposition (IAD) or ion vapor deposition (IVD) and is a version of vacuum deposition. Ion plating uses concurrent or periodic bombardment of the substrate, and deposits film by atomic-sized energetic particles. Within the jewelry and watch trade, this process is used to apply a hardwearing and durable finish to products. Bombardment prior to deposition is used to sputter clean the substrate surface. During the deposition, the bombardment is used to modify and control the properties of the depositing film. Primarily, it is used to complete accessories crafted from stainless steel. Read on and gain a new understanding of this fascinating technique.
Process
This process has quickly gained a strong following, and with reason! Ion plating is very durable compared to traditional techniques. In ion plating, the energy, flux, and mass of the bombarding species along with the ratio of bombarding particles to depositing particles are important processing variables. Experimentation has shown that this new method can be five to eight times more durable. The depositing material may be vaporized either by evaporation, sputtering (bias sputtering), arc vaporization, or by decomposition of a chemical vapor precursor chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The material used in this type of coating is ionized and vaporized through the aid of an electric arc and then forced toward the target at high speed.
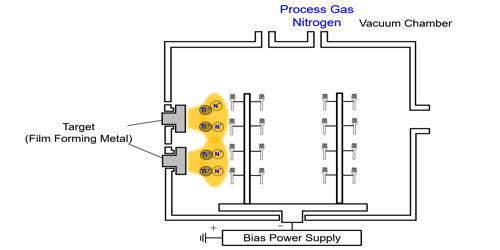
To begin, the material that will be plated, otherwise known as the substrate, must be cleaned. Foreign materials must be removed at this stage to prevent any spoiling of the finish. The energetic particles used for bombardment are usually ions of an inert or reactive gas, or, in some cases, ions of the condensing film material (“film ions”). This makes ion plated jewelry and accessories a rugged option for daily wear. Ion plating is used to deposit hard coatings of compound materials on tools, adherent metal coatings, optical coatings with high densities, and conformal coatings on complex surfaces. This process is commonly performed within a vacuum chamber or an inert gas setting.
Advantages
- Better surface coverage than other methods (Physical vapor deposition, Sputter deposition).
- More energy available on the surface of the bombarding species, resulting in more complete bonding.
- Flexibility with the level of ion bombardment.
- Improved chemical reactions when supplying plasma and energy to surface of the bombarding species.
Disadvantages
- Increased variables to take into account when compared to other techniques.
- Uniformity of plating not always consistent.
- Excessive heating to the substrate.
- Compressive stress.