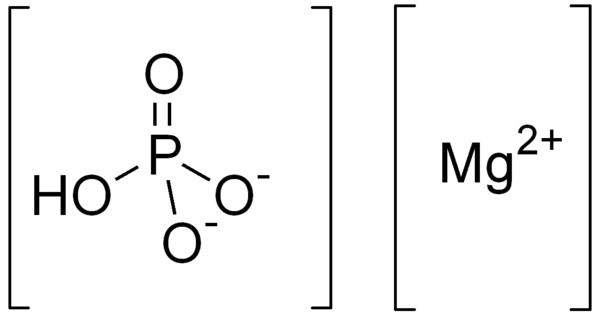
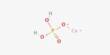
Dimagnesium phosphate is a compound with formula MgHPO4. It is a Mg2+ salt of monohydrogen phosphate. It is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula MgHPO₄. It is one of several magnesium phosphate salts and is commonly found in both anhydrous and hydrated forms. The trihydrate is well known, occurring as a mineral. It is one of the magnesium salts of phosphoric acid, and its various forms are used in food, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture.
It can be formed by reaction of stoichiometric quantities of magnesium oxide with phosphoric acid.
MgO + H3PO4 → MgHPO4 + H2O
Dissolving monomagnesium phosphate in water, forms phosphoric acid and depositing a solid precipitate of dimagnesium phosphate trihydrate:
Mg(H2PO4)2 + 3 H2O → Mg(HPO4).3H2O + H3PO4
The compound is used as a nutritional supplement, especially for infants and athletes. Its E number is E343.
Properties
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; insoluble in alcohol
- pH: Slightly basic in aqueous solution
- Elements: Magnesium (Mg), Hydrogen (H), Phosphorus (P), and Oxygen (O)
- It contains a hydrogen phosphate ion (HPO₄²⁻) bonded with magnesium ions.
Preparation and Synthesis
- Typically prepared by reacting magnesium salts (like MgCl₂) with disodium phosphate (Na₂HPO₄) in aqueous solution, followed by precipitation.
- Common in buffer systems due to its buffering capacity in physiological pH range.
Natural Occurrence
- Mineral Form: The trihydrate form of dimagnesium phosphate occurs naturally as the mineral newberyite.
- Geological Context: Newberyite is found in guano deposits, cave environments, and phosphate-rich sedimentary rocks.
Uses
- Food Industry: Used as a dietary supplement (source of magnesium and phosphate) and as a food additive (E343).
- Pharmaceuticals: Can be used in laxatives or as a buffering agent.
- Agriculture: Sometimes used in fertilizers as a magnesium and phosphorus source.
- Water Treatment: May be used in certain formulations.