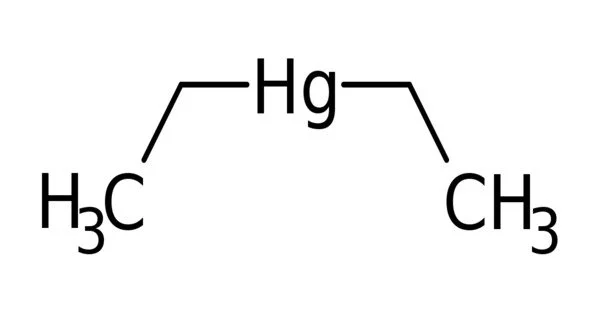
Diethylmercury is a flammable, colourless liquid that is one of the most potent neurotoxins known. This organomercury compound is said to have a slightly sweet odour, but inhaling enough fumes to detect this would be dangerous. This chemical has the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in permanent brain damage. However, it is far less toxic than dimethylmercury.
Diethylmercury, with the chemical formula (C2H5)2Hg, is a highly toxic organic compound. It is a member of the organomercury compound family, which includes compounds with a carbon-mercury bond.
At room temperature, diethylmercury is a colourless liquid with a slightly sweet odour. It is a highly volatile substance, which means it will quickly evaporate into the air. It is also soluble in organic solvents but has a low water solubility.
Synthesis
Diethylmercury can be obtained from the reaction between ethylmagnesium bromide and mercury(II) chloride.
2 C2H5MgBr + HgCl2 → Hg(C2H5)2 + MgBr2 + MgCl2
Other methods are also known.
Medical function
Diethylmercury can cross the blood-brain barrier and accumulate in the brain and nervous system once inside the body. It is directed specifically at the central nervous system and has the potential to cause severe neurological damage. Sensory disturbances, vision and hearing impairment, coordination problems, cognitive impairment, and death are all possible symptoms of diethylmercury poisoning.
Diethylmercury exposure is frequently linked to occupational hazards, such as laboratory mishaps or industrial settings. When working with or around diethylmercury, it is critical to exercise extreme caution and adhere to appropriate safety protocols.
Toxicity
Diethylmercury’s extreme toxicity is one of its most notable characteristics. It is regarded as one of the most dangerous substances known to humans. Even low levels of diethylmercury exposure can have serious health consequences. It can be absorbed through inhalation, ingestion, or contact with the skin.
Diethylmercury use has been heavily regulated or banned in many countries due to its extreme toxicity and potential for causing severe health effects. It is rarely encountered in daily life or industrial applications.