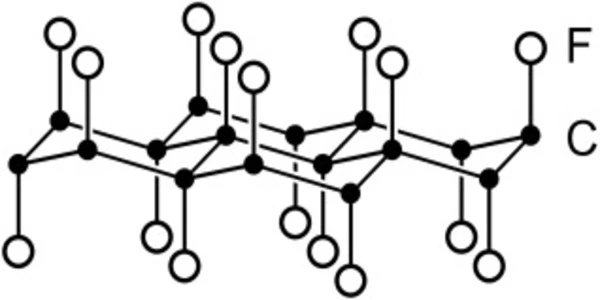
Carbon monofluoride is a material formed by the high-temperature reaction of fluorine gas with graphite, charcoal, or pyrolytic carbon powder. It is also known as polycarbon monofluoride (PMF) and graphite fluoride. It is a white powder made by fluorinating coke carbon. Because it is nonconductive, it must be combined with conductive carbon. It is a microcrystalline powder that is extremely hydrophobic. It has the CAS number 51311-17-2. It is a covalent graphite compound, as opposed to graphite intercalation compounds.
Carbon is stable in a fluorine atmosphere up to about 400 °C, but between 420 and 600 °C, a reaction occurs to produce substoichiometric carbon monofluoride, CF0.68, which appears dark grey. Stoichiometries of up to CF1.12 are formed as temperature and fluorine pressure increase. The color changes from dark grey to cream-white as the fluorine content increases, indicating the loss of aromatic character.
The fluorine atoms are arranged in an alternating pattern above and below the former graphene plane, which has buckled due to the formation of covalent carbon-fluorine bonds. At higher temperatures, carbon reacts with fluorine to produce a mixture of gaseous fluorocarbons such as tetrafluorocarbon, CF4, and tetrafluoroethylene, C2F4.
Similarly, the recently discovered carbon allotrope fullerene, C60, reacts with fluorine gas to produce fullerene fluorides with stoichiometries ranging from C60F48 to C60F48. The lithium is pressed against a nickel screen that has been expanded. The electrolytes are tetrahydrofuran and PC mixtures with lithium tetrafluoroborate as an additive. The fluorine-graphite intercalation compound, also known as fluorine-GIC, is a precursor of carbon monofluoride.
Other intercalation fluorides of carbon are:
- poly(dicarbon fluoride) ((C2F)n);
- tetracarbon monofluoride (TCMF, C4F).
Graphite fluoride is a precursor for preparation of graphene fluoride by a liquid phase exfoliation.
Application
Carbon monofluoride is used as a high-energy-density cathode material in “BR” lithium batteries. Other applications include lubricant wear reduction additives and paint weather resistance additives. Graphite fluoride is also used in rocket propellants and pyrolants as an oxidizing agent and a combustion modifier.
Carbon monofluoride is commercially available under the Carbofluor brand.