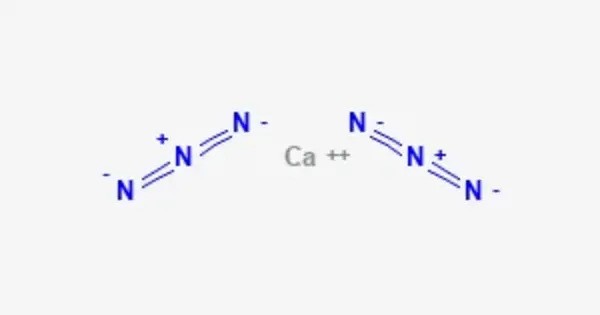
Calcium azide is a chemical compound with the formula Ca(N3)2. It is a white, crystalline substance that contains both calcium (Ca) and azide (N₃) ions. It is most commonly used as a precursor in the preparation of other azide compounds, which can be utilized in various industrial applications, such as in the production of explosives or as a source of nitrogen.
Azides, including calcium azide, are highly reactive and can be hazardous, especially when subjected to heat or shock, as they can decompose explosively to release nitrogen gas (N₂). For this reason, handling calcium azide requires careful precautions to avoid accidents.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Ca(N3)2
- Molar mass: 124.12 g/mol
- Appearance: colorless crystals
- Melting point: 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) decomposes at 150 °C
- Solubility in water: 38.1 g/100 mL (0 °C)
- Solubility: slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether, acetone
Production
It can be obtained from a distilled reaction between hydrazoic acid and calcium hydroxide.
Reactivity
Calcium azide is considered highly reactive, particularly because of the azide anion (N₃⁻), which is known for its explosive properties under certain conditions. When heated or subjected to shock, calcium azide may decompose to release nitrogen gas (N₂), and this decomposition can be violent.
Stability
Like other azides, calcium azide can be unstable under certain conditions, particularly when exposed to high heat or mechanical shock, leading to its decomposition. This makes it a potential safety hazard.
Use in Explosives
Azides, including calcium azide, are often used in detonators and other explosive applications due to their ability to decompose rapidly, releasing a large amount of gas.
Occurrences:
- Natural Occurrence: Calcium azide does not naturally occur in significant quantities in nature. It is primarily synthesized in laboratories or industrial settings.
- Industrial Synthesis: Calcium azide is typically synthesized by reacting calcium metal or calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) with sodium azide (NaN₃) in a controlled environment.
Safety
Calcium azide is sensitive to impact, in which it may detonate and ignite. Its decomposition can be triggered by heat or mechanical shock, releasing nitrogen gas (N₂), which could lead to an explosion.