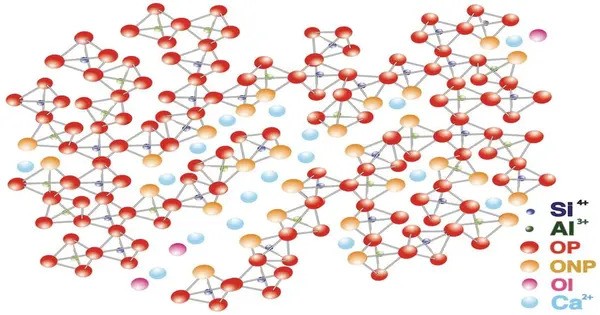
Calcium aluminosilicate, an aluminosilicate compound with calcium cations, most typically has formula CaAl2Si2O8. is a type of mineral compound that consists of calcium (Ca), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). In minerals, as a feldspar, it can be found as anorthite, an end-member of the plagioclase series. It is typically found in various forms of natural minerals or synthetic compounds, and it is important in various industrial applications, especially in the fields of construction and ceramics.
This compound can be found in some types of rocks, including certain types of volcanic ash, clay minerals, and feldspar minerals. They are typically part of a larger class of minerals called feldspars (e.g., anorthite, a calcium-rich feldspar).
Properties
- Chemical formula: CaAl2Si2O8
- High-temperature stability: These compounds can withstand high temperatures, making them valuable in heat-resistant applications.
- Chemical Stability: These compounds are generally chemically stable and can resist corrosion or breakdown in harsh environments.
- Color: Typically white, gray, or colorless, though it can have shades depending on impurities.
- Hardness: Ranges between 5.5 and 7 on the Mohs scale, which is relatively hard compared to many other minerals.
- Density: Generally falls within the range of 2.5 to 3.5 g/cm³.
- Cleavage: It often exhibit perfect cleavage along specific planes, especially in the feldspar group.
- Transparency: Most forms of calcium aluminosilicates are opaque or translucent.
Uses
As a food additive, it is sometimes designated E556. It is known to the FDA as, at under 2% by weight, an anti-caking agent for table salt, and as an ingredient in vanilla powder.
Calcium aluminosilicates are an important class of minerals, both in geological and industrial contexts. They occur widely in various geological settings, especially in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Their chemical and physical properties make them valuable in a wide range of applications, from ceramics to construction materials. Their role in geology is also significant, as they provide insight into the conditions under which rocks form and metamorphose.
Industrial Uses
- Cement and Concrete: Calcium aluminosilicate is often involved in the production of cement and other building materials, especially in high-performance or specialty cements, due to its ability to help create strong, durable materials.
- Ceramics: It is used in the manufacture of ceramics, glass, and porcelain, where it contributes to the strength and heat resistance of the final product.
- Detoxification: Calcium aluminosilicates are also used in some contexts, such as food processing, where they act as a detoxifying agent or adsorbent.