Bioplastic simply refers to plastic made from plants or other biological material instead of petroleum. Bioplastics are plastics materials produced from renewable biomass sources, such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, straw, woodchips, sawdust, recycled food waste, etc. It is also often called bio-based plastic. These are increasingly being used in industry sectors beyond bottling and packaging with many brands discovering their diversity and flexibility.
Bioplastics made from renewable resources can be naturally recycled by biological processes, thus limiting the use of fossil fuels and protecting the environment. It is a biodegradable plastic that is made or derived from biological materials
Bioplastic is a biodegradable material that comes from renewable sources and can be used to reduce the problem of plastic waste that is suffocating the planet and polluting the environment. It can be made from agricultural by-products and also from used plastics (i.e. plastic bottles and other containers) by using microorganisms. It can either be made by extracting sugar from plants like corn and sugarcane to convert into polylactic acids (PLAs), or it can be made from polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) engineered from microorganisms.
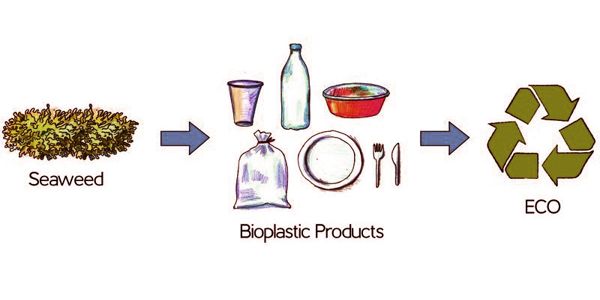
Bioplastics are usually derived from sugar derivatives, including starch, cellulose, and lactic acid. Bioplastics are driving the evolution of plastics. They are made wholly or in part from renewable biomass sources such as sugarcane and corn, or from microbe such as yeast. There are two major advantages of biobased plastic products compared to their conventional versions: they save fossil resources by using biomass which regenerates (annually) and provides the unique potential of carbon neutrality. Common plastics, such as fossil-fuel plastics (also called petrobased polymers) are derived from petroleum or natural gas.
Therefore, bioplastics are sustainable, largely biodegradable, and biocompatible. These are used for disposable items, such as packaging, crockery, cutlery, pots, bowls, and straws. Few commercial applications exist for bioplastics. Cost and performance remain problematic. Today, bioplastics have become a necessity in many industrial applications such as food packaging, agriculture and horticulture, composting bags, and hygiene.
Bioplastics are biodegradable materials that come from renewable sources and can be used to reduce the problem of plastic waste that is suffocating the planet and contaminating the environment. Beyond structural materials, electroactive bioplastics are being developed that promise to carry electric current. These have also found their use in biomedical, structural, electrical, and other consumer products.
Information Source: