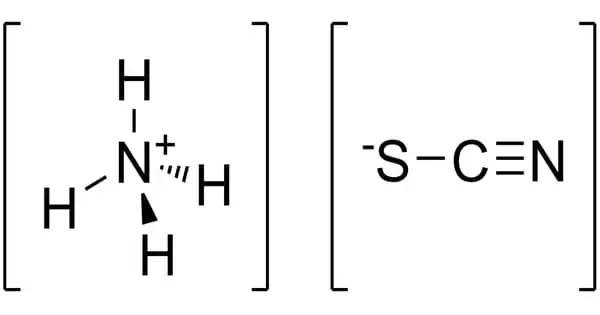Ammonium bifluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula [NH4][HF2] or [NH4]F·HF. It is produced from ammonia and hydrogen fluoride. It is an inorganic compound used in various industrial applications, particularly for its ability to etch glass and clean metal surfaces. This colourless salt is a glass-etchant and an intermediate in a once-contemplated route to hydrofluoric acid.
Properties
- Chemical formula: [NH4][HF2]
- Molar mass: 57.044 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Colourless crystals
- Density: 1.50 g cm−3
- Melting point: 126 °C (259 °F; 399 K)
- Boiling point: 240 °C (464 °F; 513 K)(decomposes)
- Solubility in water: 63g/(100 ml) (20 °C)
- Solubility in alcohol: slightly soluble
Reactivity
- It is acidic in nature due to the presence of hydrogen fluoride (HF).
- Readily decomposes to release hydrogen fluoride (HF), which is highly corrosive and toxic.
- Acts as a source of fluoride ions (F⁻) in reactions.
- Reacts with silicates and oxides, making it effective in glass etching and metal cleaning.
Production
Ammonium bifluoride is a component of some etchants. It attacks silica component of glass:
SiO2 + 4 [NH4][HF2] → SiF4 + 4 [NH4]F + 2 H2O
Potassium bifluoride is a related more commonly used etchant.
Ammonium bifluoride has been considered as an intermediate in the production of hydrofluoric acid from hexafluorosilicic acid. Thus, hexafluorosilicic acid is hydrolyzed to give ammonium fluoride, which thermally decomposes to give the bifluoride:
H2[SiF6] + 6 NH3 + 2 H2O → SiO2 + 6 [NH4]F
2 [NH4]F → NH3 + [NH4][HF2]
The resulting ammonium bifluoride is converted to sodium bifluoride, which thermally decomposes to release HF.
Ammonium bifluoride is also used as an additive in tin-nickel plating processes as the fluoride ion acts as a complexing agent with the tin, allowing for greater control over the resulting composition and finish.
Uses
- Glass etching and frosting
- Cleaning agents for stainless steel
- Metal surface treatment
- Ceramics and electronics manufacturing
- Oil well acidizing in the petroleum industry
Toxicity
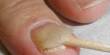
Ammonium bifluoride is toxic to consume and a skin corrosion agent. Upon exposure to skin, rinsing with water followed by a treatment of calcium gluconate is required. In water, ammonium bifluoride exists in chemical equilibrium with hydrofluoric acid and heating releases hydrogen fluoride gas.
- Highly corrosive: Can cause severe burns to skin and eyes.
- Protective gear: Gloves, goggles, and proper ventilation are essential.
- First aid: Calcium gluconate gel is used in case of skin exposure.