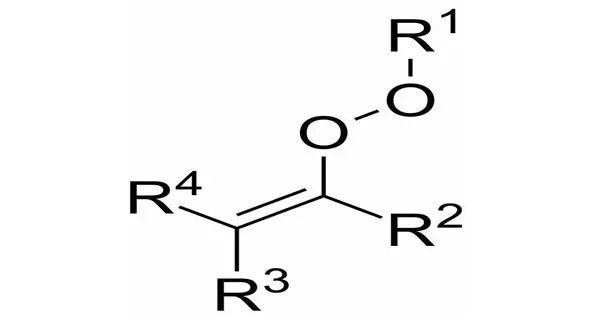
In organic chemistry, alkenyl peroxides are organic peroxides bearing an alkene (R2C=CR2) residue directly at the peroxide (R−O−O−R) group, resulting in the general formula R2C=C(R)OOR. They have very weak O-O bonds and are thus generally unstable compounds. These are generally used as initiators for polymerization reactions, particularly in the production of various plastics and synthetic rubbers.
Occurrence
In the atmosphere – Alkenyl hydroperoxides (R1 = H) have been postulated as reactive intermediates in atmospheric chemistry. They are formed via ozonolysis of alkenes in the atmosphere and form hydroxyl radicals upon decay, which play an important role in the decomposition of pollutants in the air. During day-time, hydroxyl radicals form predominantly photochemically by irradiation with light; whereas in the dark during night-time, the formation via alkenyl peroxides is believed to be their major source.
In solution – Alkenyl peroxides can be formed by acid catalyzed condensation of ketones with organic hydroperoxides or hydrogen peroxide. This has been suggested based on the characterization of the corresponding products of decomposition. Alkenyl peroxides could also occur as unwanted byproducts in the Baeyer–Villiger oxidation when using hydrogen peroxide, which would diminish the effectiveness of this reaction.
Characteristics
- Polymerization Initiation: Alkenyl peroxides are commonly used as free radical initiators in the polymerization of monomers like styrene, acrylates, and vinyl chloride. The decomposition of the peroxide generates free radicals, which can initiate the polymerization process.
- Curing Agents: Alkenyl peroxides are also used as curing agents in the production of crosslinked polymers and elastomers, particularly in the manufacturing of rubber products. The peroxide initiates the crosslinking process by forming free radicals that react with polymer chains.
Applications
The radicals formed from alkenyl peroxides can be utilized in organic radical reactions. For example, they can mediate hydrogen atom abstraction reactions and thus lead to the functionalization of C-H bonds, or they can be used to introduce ketone residues by addition of the alkenyloxyl radicals to alkenes.
Safety Considerations
Peroxides, including alkenyl peroxides, can be highly reactive and may decompose explosively under certain conditions, especially if exposed to heat, shock, or contamination. Proper storage and handling are crucial to prevent accidents.