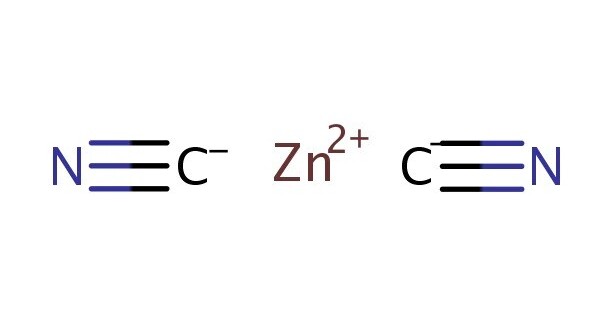Zinc cyanide is the inorganic compound with the formula Zn(CN)2. It is an inorganic compound that consists of zinc and cyanide ions. It’s often encountered in industrial processes and applications, particularly in electroplating and metal finishing. It is a white solid that is used mainly for electroplating zinc but also has more specialized applications for the synthesis of organic compounds.
It appears as a white solid and is soluble in water. Zinc cyanide can release toxic cyanide gas when it comes into contact with acids. Besides electroplating, it may be used in some organic synthesis processes, as a catalyst, or in mining applications to separate metals from ores. Due to its toxicity, the use and disposal of zinc cyanide are regulated in many countries to prevent environmental contamination and health hazards.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Zn(CN)2
- Molar mass: 117.444 g/mol
- Appearance: white solid
- Density: 1.852 g/cm3, solid
- Melting point: 800 °C (1,470 °F; 1,070 K) (decomposes)
- Solubility in water: 0.0005 g/100 mL (20 °C)
- Solubility: attacked by alkalies, KCN, ammonia
Chemical properties
Typical for an inorganic polymer, Zn(CN)2 is insoluble in most solvents. The solid dissolves in, or more precisely, is degraded by, aqueous solutions of basic ligands such as hydroxide, ammonia, and additional cyanide to give anionic complexes.
Occurrences
- Mining and Metallurgy: May occur as a byproduct in the extraction of gold and silver from ores.
- Environmental Concerns: Can be found in waste streams from industries that use cyanide for processes such as gold mining, posing risks to human health and ecosystems.
Industrial Applications
Used in electroplating, as a catalyst, and in the synthesis of other chemicals. It can be involved in processes where zinc and cyanide compounds are present.
Safety Considerations
Due to its toxicity, handling zinc cyanide requires strict safety precautions, including appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination.