Vanadium carbide is the inorganic compound with the formula VC. It is an extremely hard refractory ceramic material. With a hardness of 9-9.5 Mohs, it is possibly the hardest metal-carbide known. Vanadium carbide (VC) coating technology provides a superior protective coating for steel surfaces and eliminates the need for multiple heat-treatment steps during processing, thereby eliminating harmful gas emissions. It is of interest because it is prevalent in vanadium metal and alloys.
Vanadium Carbide is an extremely hard refractory ceramic material. It is available in numerous forms and custom shapes including Ingot, foil, rod, plate, and sputtering target.
Physical properties
Vanadium Carbide has an elastic modulus of approximately 380 GPa. The transition metal carbides have very high melting points, hardness, and high-temperature strength. These materials also exhibit good electrical and thermal conductivities.
- Compound Formula: VC
- Molecular Weight: 62.95
- Appearance: Black Powder
- Melting Point: 2,810°C (5,090° F)
- Boiling Point: N/A
- Density: 5.77 g/cm3

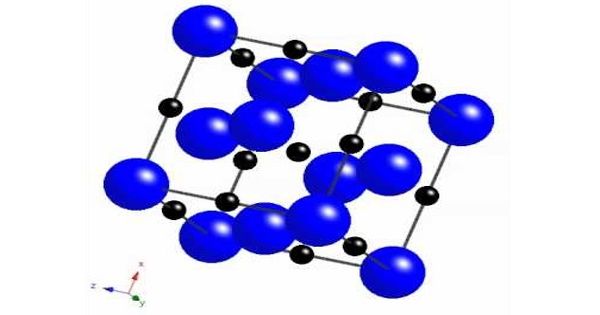
Structure and preparation
Transition metal carbides have attracted continuing interest due to their excellent physical properties and wide engineering applications. Being isomorphous with vanadium monoxide, it crystallizes in the rock salt structure. Because VC and VO are miscible, samples of VC typically contain an impurity of the oxide. Vanadium Carbide is available in numerous forms and custom shapes including Ingot, foil, rod, plate, and sputtering target.
It is produced by heating vanadium oxides with carbon at around 1000°C. Vanadium carbide can be formed in the (111) orientation when formed by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Although VC is thermodynamically stable, it converts to V2C at higher temperatures. The flexibility in stoichiometry leads to rich chemical and physical behaviors and provides a lot of candidates for materials design.
Uses
Vanadium carbide is used as an additive to cemented carbide, to refine the carbide crystals and thereby get an increased hardness of the inserts. It protects steel surfaces with a thick, well-controlled layer of VC while eliminating the need for multiple heat-treatment steps that increase energy use and the chance of production defects.