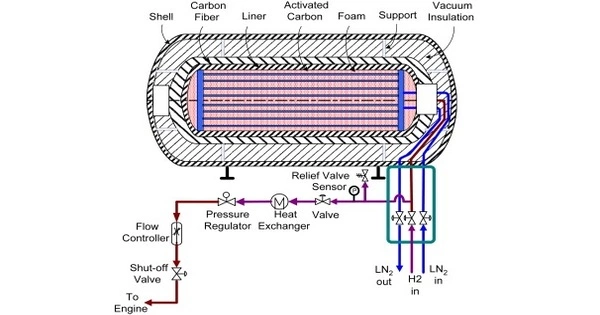
Cryo-adsorption refers to the process of adsorbing gases or other substances onto a solid surface at very low temperatures, typically below -150°C. The technique is often used in various scientific and industrial applications, such as in vacuum technology, materials science, and gas storage.
Cryo-adsorption is a process in which gas molecules are adsorbed onto a solid surface at very low temperatures, typically below 100 Kelvin (-173°C). The adsorption of gas molecules onto a solid surface at cryogenic temperatures can result in high adsorption capacities, making it an attractive method for gas storage and separation.
Principle
Cryo-adsorption is based on the principle of physical adsorption, where molecules from the gas phase are attracted to the surface of a solid material and adhere to it through weak intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces. At cryogenic temperatures, the adsorption process is enhanced due to the lower thermal energy of the gas molecules, which allows for stronger binding to the surface.
Cryo-adsorption is commonly used in the production and purification of gases, such as hydrogen and helium, which have low boiling points and are difficult to store at ambient temperatures. The process involves exposing the gas to a solid adsorbent material, such as activated carbon or zeolites, at cryogenic temperatures. The gas molecules then adhere to the surface of the adsorbent, effectively removing them from the gas stream.
Application
Cryo-adsorption is a method for storing hydrogen in which gaseous hydrogen is physically adsorbed on porous material, most commonly activated carbon, at cryogenic temperatures (150—60 K). The storage density achieved is comparable to that of liquid-hydrogen (LH2) storage systems and compressed-hydrogen (CGH2) storage systems.
Cryo-adsorption is commonly used in vacuum technology, where it is used to remove trace gases from vacuum chambers or to purify gases. It is also used in the field of materials science, where it can be used to study the interaction of gases with various surfaces or to create thin films of materials. Additionally, cryo-adsorption has potential applications in the storage of gases, such as hydrogen, which can be adsorbed onto high surface area materials for use as fuel in fuel cells.
Cryo-adsorption has applications in a range of fields, including space exploration, where it is used to store and separate gases in spacecraft, and in the production of high-purity gases for semiconductor manufacturing. It is also used in research to study the properties of adsorbent materials and the behavior of gas molecules at cryogenic temperatures.