Uranium boride (UB2), a uranium-boron combination, is a highly stable glassy boride substance that is insoluble in water. It is employed in a variety of commercial and scientific applications due to its unique features. Uranium boride compounds can have excellent hardness, melting temperatures, and thermal and chemical stability. They are frequently investigated for applications in nuclear materials, high-temperature ceramics, and as catalysts in specific chemical reactions.
It is being studied as a nuclear fuel material due to its high density and thermal conductivity.
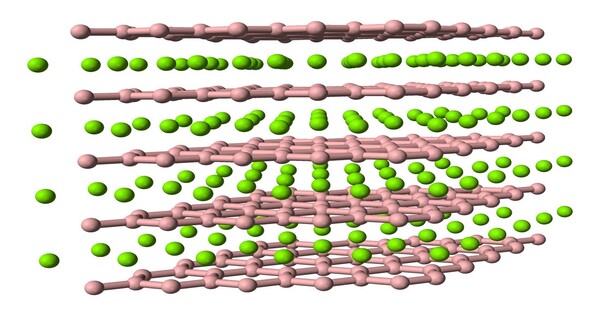
Properties
It is a hard, dense material that could be used in a variety of high-wear applications. Uranium borides have strong thermal and electrical conductivity, though particular values vary depending on the phase and structure. It can be reactive under certain situations, especially when exposed to moisture or high temperatures. It may also be radioactive due to its uranium content.
- Chemical formula: UB2
- Molar mass: 259.651 g/mol
- Density: 12.7 g/cm3
- Melting point: 2,430 °C (4,410 °F; 2,700 K)
It is being investigated as a component in high entropy alloys and as a technique of immobilizing uranium-based radioactive waste to make it safe for long-term storage. It has certain applications in endocurietherapy, a type of radiation therapy in which radioactive microspheres are implanted directly into the treatment site and allowed to remain for a lengthy period of time. This class of material may also be used because it is not attacked while in situ.
Applications
- Nuclear Industry: Uranium boride can be used as a neutron absorber or moderator in nuclear reactors. Its ability to absorb neutrons makes it useful in controlling the nuclear fission process.
- High-Temperature Materials: It can be used in high-temperature applications due to its stability and resistance to thermal degradation. This includes use in aerospace and other high-temperature environments.
- Ceramics: Uranium boride is sometimes used in the production of advanced ceramics, which are needed for various high-performance applications.