Introduction
Training & Development practice under the HRM. Training & Development practice
Develop the Human Resource by their skill, performance, efficiency, technical know how policy making, planning, decision and advance thinking etc.
Training & Development:
Training:
Training is the acquisition of new skills and knowledge relevant to a job. Development involves the growth of an individual\’s wider education and capabilities within a field of employment.
- Induction training familiarizes new employees with their role and responsibilities. Colleagues are introduced, systems explained and the expectations of the job are clarified.
- On-the-job training is arranged in the workplace through instruction and observation.
- Off-the-job training takes employees away from the immediate workplace. It may be \’in-house\’ using the employer\’s facilities or \’out-house\’ and provided by another company or college/university.
Development:
Development has a broader focus on learning and relates to a career rather than to a job. It emphasizes the employee\’s potential to acquire more capabilities.
The government supports training and development through modern apprenticeships which give young people vocational skills through a mix of on and off-the-job training. The Investors in People award requires firms to demonstrate their commitment to training and career development for staff.
Objective of Training & Development
Needs result in training and development objective, which should state the desired behavior and the condition under which it is to occur. These stated objectives then become standards against which individual performance and the program can measured.
For example, the objective for airline reservationists might be states as follows:
- Provide flight information to call in customers within thirty second.
- Complete a one-city round-trip reservation in two minutes after all information has been obtained from the customer.
Specific, measurable, time –targeted objectives like those listed above for a preservationist give the trainer and the trainee specific goals that can be used to evaluate their success .If the objective are not met, failure gives the HR department feedback on the program and the participants.
Importance of Training & Development:
Optimum Utilization of Human Resources – Training and Development helps in optimizing the utilization of human resource that further helps the employee to achieve the organizational goals as well as their individual goals.
Development of Human Resources – Training and Development helps to provide an opportunity and broad structure for the development of human resources’ technical and behavioral skills in an organization. It also helps the employees in attaining personal growth.
Development of skills of employees – Training and Development helps in increasing the job knowledge and skills of employees at each level. It helps to expand the horizons of Human intellect and an overall personality of the employees.
Productivity – Training and Development helps in increasing the productivity of the employees that helps the organization further to achieve its long-term goal. Team spirit – Training and Development helps in inculcating the sense of team work, team spirit, and inter-team collaborations. It helps in inculcating the zeal to learn within the employees.
Organization Culture – Training and Development helps to develop and improve the organizational health culture and effectiveness. It helps in creating the learning culture within the organization.
Organization Climate – Training and Development helps building the positive perception and feeling about the organization. The employees get these feelings from leaders, subordinates, and peers.
Quality – Training and Development helps in improving upon the quality of work and work-life.
Healthy work environment – Training and Development helps in creating the healthy working environment. It helps to build good employee, relationship so that individual goals aligns with organizational goal.
Health and Safety – Training and Development helps in improving the health and safety of the organization thus preventing obsolescence.
Morale – Training and Development helps in improving the morale of the work force.
Image – Training and Development helps in creating a better corporate image.
Profitability – Training and Development leads to improved profitability and more positive attitudes towards profit orientation.
Training and Development aids in organizational development i.e. Organization gets more effective decision making and problem solving. It helps in understanding and carrying out organizational policies
Training and Development helps in developing leadership skills, motivation, loyalty, better attitudes, and other aspects that successful workers and managers usually display.
The Five-Step of Training and Development:
- Needs analysis step, identifies the specific job performance skills needed, assesses the prospective trainees skills, and develops specific, measurable knowledge and performance objectives based on any deficiencies.
- Instructional design ,you decide on ,compile, and produce the training program content ,including workbooks, exercise ,and activities ,here you’ll probably use technique like those discussed in this chapter ,such as on the job training and computer assisted learning.
- Validation step, in which the bugs are worked out of the training program by presenting it to a small reprehensive audience.
- Is to the implement the program, by actually training the targeted employee
Group.
- Is an evaluation step, in which management assesses the program’s success or failures.
Methods of Training
There are various methods of training which can be divided into cog native and behavioral methods .Trainers need to under stand the pros & cons of each method also its impact on trainees keeping their background and skill in mind before giving training.
Cog native Methods: This method is more of giving theoretical training to the trainees. The various methods under cognitive approach provide the rules for how to do some thing, or verbal information, demonstrate, relation ships among concepts, etc, these methods are associated with changes in knowledge and attitude by stimulating learning.
The various methods that come under cog native approach are,
- on the job training.
- Apprenticeship training
- Informal learning
- Job instruction training
- Lectures
- Audiovisual- based training
- Simulated training
Behavioral Methods: These methods are more of giving practical training to the trainees. The various methods under behavioral approach allow the trainee to behavior in a real fashion. These methods are best used for skill development.
The various methods that come under behavioral approach are,
1. Games & simulations
2. Behavior-modeling
3. Business games
4. Case studies
Managerial on-the-job training:
a. job rotation
b. Coaching
c. Action learning
Off- the-job management training development:
a. The case study method
b. Management games
c. Outside seminars
d. University –related programs
e. Role playing
ROLE OF TRAINING
History of Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited (AIBL ):
Bangladesh is one of the largest Muslim countries of the world. The population of the country is deeply committed to Islamic way of life as enshrined in the Holy Quran and Sunni. Naturally it remains a deep cry in their hearts to fashion and design their hearts to fashion and design their economic lives in accordance with the precepts of Islam. Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited Limited. The prime objective of Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited is to serve the people for attainment of their economic goal and success in life here and hereafter. AL-ARAFAH ISLAMI BANK LIMITED stands not only for material well being but also for ethical development of its customers. The incorporation of AIBL on May 1995 is the true reflection of this inner urge of its people, which started functioning with effect from June 18, 1995. It is committed to conduct all banking and investment activities on the basis of interest-free profit-loss sharing system. In doing so, it has unveiled a new horizon and ushered a new silver lining of hope towards materializing a long cherished dream of the people of Bangladesh for doing their banking transactions in line with what is prescribe by Islam. Alarafah Islamic Bank Limited has by now earned the unique position of a leading private commercial bank in Bangladesh.
“Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited” offers the full range of banking services for personal and corporate customers, covering all segments of society within the framework of Banking Company Act and rules and regulations laid down by our central bank. Diversification of products and services include Corporate Banking, Retail Banking and Consumer Banking right from industry to agriculture, real estate to software and is backed by the latest technology.
The Bank is being managed by a group of highly experienced professionals with diversified experience in finance and banking The Bank has already achieved tremendous progress within only five years. The bank has already ranked as one of the quality service providers & is known for its reputation.
By now, the Bank established correspondent Banking relationship with 18 Banks covering their global network of 385 branches/units of International repute at different important locations. It also established accounting relationship with 10 Banks and maintaining 22 NOSTRO Accounts in 8 (eight) major Currencies at different convenient locations.
The Bank is managed by a Team of professional Executives and Officials having profound banking knowledge & expertise in different areas of management and operation of Banks. During the short span of time, Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited so far introduced a good number of attractive deposit products to broaden the resource base and also Investment products to deploy the deposit resources so mobilized. Some more schemes covering the deposits, Investments & Services will be introduced gradually in near future suiting to the taste and requirement of the clients. The Bank has a strong Shariah Council consisting of prominent Ulama, Fuquah & Economists who meet periodically to confer decisions on different Shariah issues relating to Banking Operation & to address them and to give necessary guidance to the management on Shariah Principle. Since inception, Bank has been performing in all the sectors i.e. general Banking, Remittance, Import, Export & Investment. All our branches are fully computerized having on line Banking facility for the clients.
Company Profile:
Company Profile in Brief | |
| Name | Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited Limited |
| Registered Office | 36Dilkusha(6-9) ,C/A,Dhaka-1000 |
| Legal Status | Public Limited Company. |
| Nature of Business | Commercial, Corporate, Investment & Retail Banking |
| First meeting of the promoters held on | 4th September, 1995. |
| Date of Certificate of Incorporation | 1st May, 1995. |
| Date of Certificate of Commencement of Business | 27 September, 1995. |
| Banking License received on | 18th April, 1995. |
| First Branch License received on | 24th April,1995 |
| Inauguration held on | 27th September, 1995. |
| Authorized Capital | Tk.5000000000.00 crore. |
| Paid up Capital | Tk.4677280000.00 crore. |
| Number of Branches (as on 20.012.2012) | 95 |
| Auditors | Howladar Yunus & Company. |
| Board of Director | 20 |
| No. of Sponsor Directors | 19 |
| Meeting of Board of Directors | 229. |
- Board Committees: The Board responsibility of each committee is determined by the Board of Directors who also decides on the composition of each committee. MD Badiur Rahman is the chairman of AIBL. Sharker Md Shameem Iqbal is the vice chairman
- Executive committee: All routine matters beyond delegated powers of management are decided upon by or routed through the Executive Committee, subject to ratification by the Board of Directors.
- Audit committee: All matters relating to the principles, policies, financial inquiries etc. for operation and management of the Bank are recommended by the Committee to the Board of Directors.
- Shariah Council: As per Articles of Association of the company and Islamic Shariah Council for 5th Bank has been constituted. The Council plays a vital role in advising and guiding on the implementations and compliance of Shariah principles in all activities of the Banks particularly on the modes of Investment. Mufti Abdur Rahman is the chairman of shariah council.
Branch Information of AIBL :
The Bank commenced its business on june 18, 1995 by opening its 1st branch is Dhaka Main branch at 36, Dilkusha, Dhaka obtaining the license from Bangladesh Bank, the central bank of Bangladesh. The bank opened 5 (five) branches in 1995, 6 (six) branches in 1996, 8 (eight) branches in 1997, 11 (two) branches in 1998, 4 (four) branches in 1999, 16 (sixteen) branches in 2002 & 2007. Up to September 31, 2008 AIBL established 27 branches and now 95 branches to all over the country to give a cordial service to their customers. Some of branches locations are given bellow
Table : Branches Location
| SL. No. | Name of the Branches | Location & Address |
| Motijheel Branch | 161,Motijheel C/A, Dhaka-1000. | |
| Moloby Bazar Branch | 3, Moloby Bazar , Dhaka-1000. | |
| VIP Road Branch | 86,VIP Road, Dhaka-1OOO. | |
| Motijheel Corporate Branch | 125,Motijheel, C/A,Dhaka | |
| Nababpur Road ,Branch | 85/87Nababpur Road, Dhaka ,1100 | |
| North South Road Branch | 96,Saheed Sayd Nazrul Islam Sarani,Bongshal Dhaka – 1100 | |
| UttraModelTown Branch | House 13,Road14/a,Sector-4, Uttra,Dhaka-1203 | |
| New Elephant Road Branch | 91 New Elephant Road ,Dhaka 1205 | |
| Banani Branch, | 16,Kamal Ataturk Avenue Banani, Dhaka | |
| Mirpur Branch- | 5/H.G.Daruls Salam Road,Mirpur-1Dhaka 1216 |
| Mouchak Branch | 76,D.I.T, Road,Malibhag Dhaka1217 |
| Dhanmndi Branch-
| 54/1Road4/1,Shat Mashjid Road, Dhaka 1209 |
| MohammadPur Krishi Market Branch-
| 32/8 Tazmahal road,Mohammadpur, Dhaka1207 |
| Dilkusha Branch- | 63, Dilkusha C/A Dhaka 1000 |
| Islampur Branch | 29-31 Islampur Road, Dhaka-1100 |
| Progati Sarani Branch- | 133/3,Middle Badda, Dhaka-1212 |
| Jatra Bari Branch
| 6 sahied Faruk Road,West Jatra Bari, Dhaka,1204 |
| Joydevpur Chowrasta Branch- | Khaleque Complex (1st floor), Joydevpur Chowrasta, Gazipur |
| Kawran Bazar Branch-
| T K Bhaban, 13 Kazi Nazrul Islam Avenue, Kawran Bazar, Dhaka |
| Keranigonj Branch
| Ma Plaza (1st Floor), Shohid Nogar, Karanigonj, Dhaka |
| Madhabdi Branch, Norsingdi | Jalpotti Road, Vill-Choto Madhabdi,Pauroshava & P.S.- Madhabdi,Dist: Norsingdi. |
| Mawna Branch
| N.S. Bhaban (1st Floor), Mawna Chowrasta, Sreepur, Gazipur |
| Mirpur Branch | 230, Senpara Parbata, Mirpur-10, Dhaka |
| Mohakhali Branch | IsmailMansion (Ground Floor), 32 Mohakhali C/A, Wireless Gate, Gulshan, Dhaka-1212 |
| ||
| Mymensingh Branch
| Noor Fatema Tower (1st Floor), 25, Swadeshi Bazar, Mymensingh |
| Narayanganj Branch
| OsmanTower, 56/1, S.M. Maleh Road, Narayangonj |
| Nawabpur Road Branch
| FazlurRahmanPlaza(1st Floor), Holding No:-218, Nababpur Road, Dhaka. |
| Panthapath Branch | ENATower, Di-Olie (1st floor), 57/3, 57/4, Lake Circus Road, Kolabagan, Dhanmondi, Dhaka-1212 |
| Savar Branch
| Bismillah Super Market, 71/1 and 72/1, Bazar Road, Savar, Dhaka |
| Shatmasjid Road Branch
| Khuda Buksh Foundation (1st Flr.), Road No. 11/A, House No. 99, Dhanmondi, Dhaka – 1209 |
|
| |
| Uttara Ladies Branch
| Solar TradeCenter (1st & 2nd Floor), Plot # 16, Sector # 11, Garib-E-Newaz Avenue, Uttara, |
| Vatara Branch | 311, Progoti Sarani, Nayanogor, Baridhara, Badda, Dhaka |
| Sylhet Branch
| Al-FalahTower (1st floor), Dhupadighir Purbopar, Kotowali, Sylhet |
| Cox’s Bazar Branch | A. B. Super Market (1st Floor), 145 Laldighirpar, Cox’s Bazar |
| Comilla Branch
| Salahuddin Complex(1st & 2nd Floor), Monohorpur, Chowmuhoni, Laksam Road, Comilla |
| Jessore Branch | Sadhinata Bhaban (1st Floor) Holding no: 91, M.K. Road. Kotawaly, Jessore |
| Khulna Branch | United Tower(1st and 2nd Floor), 4 KDA Avenue, Khulna |
| Kushtia Branch | 7 N. S. Road (1st & 2nd floor), Kushtia Sadar, Kushtia. |
| Rajshahi Branch
| HabibPlaza (1st Floor), Holding # 111 Shaheb Bazar, Zero Point, Rajshahi |
| Rangpur Branch
| Mr. Md. Abu Sayeed Assistant Vice President M.H. Rashid Shopping Complex (2nd & 3rd Floor), 88 Station Road, Rangpur |
| Bogra Branch
| Nurul Haque Tower(1st Floor), 357/395, Boro Gola Mor, Bogra |
| Barisal Branch
| HawladarPlaza, 475 K. B. Hemayet Uddin Road (1st & 2nd floor), Barisal |
Mission
- To provide quality services to customers.
- To set high standards of integrity.
- To make quality investment.
- To ensure sustainable growth in business.
- To ensure maximization of Shareholders’ wealth.
- To extend our customers innovative services acquiring state-of-the-art technology blended with Islamic principles.
- To ensure human resource development to meet the challenges of the time.
Vision:
To be the unique modern Islami Bank in Bangladesh and to make significant contribution to the national economy and enhance customers’ trust & wealth, quality investment, employees’ value and rapid growth in shareholders’ equity.
Strategy
- To strive for customers best satisfaction & earn their confidence.
- To manage & operate the Bank in the most effective manner.
- To identify customers needs & monitor their perception towards meeting those requirements.
- To review & updates policies, procedures & practices to enhance the ability to extend better services to the customers.
- To train & develop all employees & provide them adequate resources so that the customers needs are reasonably addressed.
- To promote organizational efficiency by communicating company plans, polices & procedures openly to the employees in a timely fashion.
- To cultivate a congenial working environment.
To diversify portfolio both the retail & wholesale markets.
Motto:
Committed to Cordial Service.
The organizational Structure of AIBL :
The objective of organizational structure and corporate governance of Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited . is to establish a strong, customer- oriented and transparent Management.
Table : Corporate Management of AIBL
Top Management
|
|
|
Executive Level Management |
|
Mid Level Management |
|
Junior Level Management |
|
Organizational Chart of AIBL :
Board of Director
Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited ‘s Board of Directors consists of the following posts
- Chairman- Badiur Rahman
- Vice Chairmen- Sarker Md Shameem Iqbql
- Managing Director- Ekramul Haque
Board Of Director Shariah And Fatwa
- Chairman Mufti Abdur Rahman
- Total Member Five Of Shariah Council
Audit Committee:
AIBL ‘s audit committee is made up of 3 individuals Chairman and two members.
Shariah Council:
Shariah Council of the Bank is playing important role in guiding and supervising the implementation and compliance of Islamic Shariah principles in all activities of the Bank since its very inception. The Council, which enjoys a high status in the structure of the Bank, consists of prominent ulema, reputed banker, renowned lawyer and eminent economist. Members of the Shariah Council meet frequently and deliberate on different issues confronting the Bank on Shariah matters. They also conduct Shariah inspection of branches regularly so as to ensure that the Shariah principles are implemented and complied with meticulously by the branches of the Bank.
Information of AIBL NORTH SOUTH ROAD Branch:
The branch was established 26th September, 2004, it is situated at the floor of Saheed Nazrul Islam Avenue, North South Road, Dhaka-1100. The bank is designed under one floor. It has been providing Islam Banking Services for the customers of North South Road, Bangshal, area.
Department of the Branch:
- Customer Care Department
- General Banking Department
- Cash Department
- Foreign Trade Department
- Investment Department
- Clearing Department
- Remittance Department
Introduction :
Employee’s are the core resources of any organization, without them, one can not run their organization, and human resources is conducted with the growth of development of people toward higher level of competency, creativity and fulfillment. It help employee’s become better more responAIBL e person and then it tries to create a climate in which they contribute to the limits of their improved abilities. It assumes that expanded capabilities and opportunities for people with lead directly to improvements in operating effectiveness. Essentially, the human resource approach means that people better result. Bank always determine what jobs need to be done, and how many and types of workers will be required.
Human Resource Department is responAIBL e for the main dimension of people of the organization. It is responAIBL e for hiring competent people, training them, helping them perform at high levels and mechanisms to ensure that these employees maintain their productive affiliation with the organization. Human Resources Department of Bank Limited is solely responAIBL e mainly for recruitment, training and development, ensuring compensation and benefits of staffs, performance appraisals and rewards. With all those core functions Human Resources Department linkage its operations meet the organization’s objectives.
Human Resources Department of Bank Limited :
Human resources Department of is one of the most valued departments with the responsibilities of staffing, training and development, organization development, performance appraisals, rewarding, control and maintenance etc. With the start of The Human Resources Department of experienced executives to carry out the whole responsibilities. The Human Resources Department of stands in its Head Office at Motijil, C’heni Shilpo Bhaban under the direct supervision of the top management.
Organization of the Human Resources of BANK:
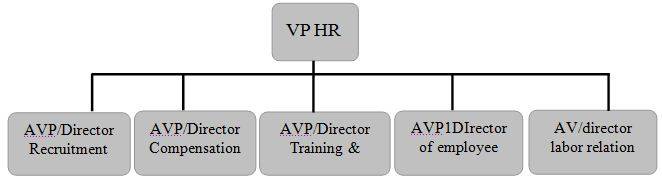
Fig: Structure of HR Department in a Large Organization
Objectives of the Human Resources Department of Bank:
The objective of HRM can be described as follows-
- To hire the right person for the job
- To reduce employee turnover
- To motive people to perform at high effort levels.
- Not to waste time with useless interviews.
- To remove unfair labor practices.
- To maintain a high morale & better human relations inside the origination.
- To maintain organizational peace.
- To attract competent people and retain them in the organization.
- To recognize and satisfy individual needs.
Basic Principles of HRM:
- Treat people with respect and dignity;
- Deal with people as complete individuals.
- Treat all employees with justice.
- Provide people with justice.
- Make people feel that they are most valuable asset for the organization.
- Rewards should be earned, not given.
- Not to underestimate the potentials of people.
- Provide people with all relevant information.
Functions of the Human Resource Department:
To control the administration of human resources of the bank
To access and collect compatible personnel who will be perfect for the bank
To take program and implement for developing human resources.
To make appointment, promotion and appraising skill of officer and stuff
To maintain relationship with government and other institution
To communicate with e union scrutinizing their demands
To give loan for house building, car, motorcycle and ensure their proper utilization
To give medical facilities to the staff.
To coordinate and evaluate the branch office
To prepare and implementation policy about human resources and related activities.
To perform the activities assigned by the department head
Define training and development:
Training to new employees is important for the reason that they need to acquire basic
skills related to the particular job in which he is employed and development means aims to increase abilities in relation to some future position or job-usually management.
Objectives of training:
Like every organization, Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited and the employees or human resources of this organization have some objectives. The organizational and individual objectives are complementary. So a training program is directed toward the accomplishment of both organizational and individual objectives. We can classify the objectives in two major headings.
Objectives of training related to Bank:
- Achieving efficiency in operation.
- Improving knowledge on new method.
- Informing the banking policy
- Providing knowledge on bank-customer relationship.
- Change of attitude toward the job.
- Reduction of employee turn-over.
- Improving quality of work.
Objectives of training related to individual:
1. Reducing inherent fear about jobs: Training is reducing inherent fear about jobs.
2. Updating Knowledge: Technological advancement, business environmental changes and new management philosophies have now made it imperative for the organization to renew and update the knowledge and skills of the employees so that they do mil become redundant for obvious functional incompetence. The first and foremost need for manpower training therefore, is to renew and update knowledge and skills of employees to sustain their effective performance and so also to develop them for future managerial positions.
3. Avoiding Obsolescence: Recent economic liberalization programs of Government of India is necessitating Organizational restructurings, which inter alia, calls for training the employees, irrespective of their functional level, for their redeployment in restructured jobs. Therefore, the second important need for training is to avert functional obsolescence.
4. Improving Performance; Continuous training being required to renew and update knowledge and skills of employees, it makes them functionally effective. The- third need is therefore, to make employees effective in their performance through continuous training.
5. Developing Human Skills: Apart from emphasizing on technical and Conceptual skills, new training programme also emphasize on developing human skills of employees. Such human skill is necessary forEffective interpersonal relations and sustaining healthy work environment. This need for training therefore also cannot be altogether ignored.
6. Imparting Trade-specific Skills: In industrial employment, the convention is to recruit workers and employees through compulsory apprenticeship training- Such apprenticeship training enables an organization to impart industry and trade specific skills to workers. This also, therefore, is an important need for manpower training.
7. Stabilizing the Workforce: Throughout the world the importance of training is now increasingly felt for stabilizing the workforce to withstand the technological change and for making the organization dynamic in this changed process. Management theorists now unanimously agree that it is the responsibility of the organization to train and develop their manpower as continuous process.
Methods of Training used by, Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited :
Methods are the ways through which. employees are trained. JAM I1Nn Bank Limited uses several methods of training depending on the situation and training objectives. However, the methods of training can primarily classify into two types. On-the -job Training (0.1T) means having a person learn a job by actually doing it. every employee, from mailoorm clerk to company president, gets on the job training when he or she joins a firm. In many firms, OJT is the only training available.
The most familiar type of on the job training is the coaching or understudy method. Here, an experienced worker or the trainee’s supervisor trains the employee. At lower levels, trains may acquire skills by observing the supervisor. But this technique is widely used at top-management level too. A potential future CEO might spend a year as assistant to the current CEO, for instance. Job rotation, in which an employee (usually a management trainee) moves from job to job at planned intervals, is another OJT technique.There are some steps to help insured OJT Success
Step :1 Prepare the Learner:
1. Put the learner at ease- relieve the tension.
2. Explain why he or she is being taught,
3. Create interest, encourage – encourage find out whit the learner already knows about this or other jobs.
4. Explain the whole job and relate it to some job the worker already knows.
5. Plane the learner is dose is the normal working position as posAIBL e.
6. Familiarize the worker with equipment, materials, tools, and trade
Step 2: Present the Operation:
1. Explain quantity and quality requirement?
2. Go through the job at the normal work pace.
3. Again go through the job at a slow pace several times; explain the key points.
4. Have the learner explain the steps is you go through the job at a slow pace,
Step :3 Do a Tryout:
1. Have the learner go though the job several times explaining: slowly, explaining each step to you. Correct mistakes and mistakes and, if necessary, do some of the complicated steps the first few times.
2 Run the job at the normal pace.
3. Have, the learner do the job, gradually building up skill and speed.
4. As soon as the learner demonstrates ability to do the job, let the work begin, but don’t abandon him or her.
Step: 4. Follow Up:
1. Designate to whom the learner should go for help
2. Gradually decrease supervision, checking work from time to time against quality and quantity standards.
3. Correct faulty work patterns before they become a habit. Show why the learned method is superior.
4. Compliment good work; encourage the worker until he or she is able to meet the quality and quantity standards.
1. Apprenticeship Training:
More employers are implementing apprenticeship programs, an-approach that began in the middle Ages. Apprenticeship training is a structured process which people become killed workers through a combination of classroom Instruction and on-the job training. It is widely to train individuals for many occupations. It traditionally involves having the learner/apprentice study under the tutelage of a master craftsperson.
Several U.S. facilities currently use this approach. For example, the siemens Stromberg-Carlson plant in Florida has apprenticeships for adults and high school students for electronics technician jobs.
2. Informal Learning:
Employers should not underestimate the importance or value of informal training. Surveys form the American Society for Training and Development estimate that as much as 80% of what employees learn on the job they learn not through formal training programs but through informal means, including performing their jobs on a dally basis in collaboration with their colleagues.
Although managers don’t arrange informal learning, threes still a lot they can do the ensure that it occurs. Most of the steps are simple.
3. Job Instruction Training;
This is training through step-by-step learning. Usually steps necessary for a job are identified in order of sequence and an employee is exposed to the different steps of a job
by an experienced trainer.
Managerial On-the-Job Training:
On -the – job training is not just for non managers. Managerial on -the -job training methods include job rotation the coaching/understudy approach, and action learning.
1. Job Rotation:
Job rotation means moving management trainees from department to department to broaden their understanding of all parts of all parts of the business and to test their abilities. The trainee – often a resent college graduate may spend several months in each department. The person may just be an observer in each department, but more commonly gets fully involved in its operations. The trainee thus learns the department’s business by actually doing it, while discovering what jobs he or she prefers.
2. Coaching/Understudy Approach:
Here the trainee works directly with a senior manager or with the person he or she is to replace, the latter is responAIBL y for the trainee’s coaching. Normally, the understudy relieves the executive of certain responsibilities, giving the trainee a chance to learn the job.
3. Action Learning:
Action learning programs give managers and others released time to work full-time on projects, analyzing and solving problems in departments other than their own. The basics of a typical action learning program include. Carefully selected teams of five to 25 members; assigning the teams real world business problems that extend beyond their usual areas of expertise and structured learning through coaching and feedback. The employer’s senior managers usually choose the projects and decide whether to accept the teams’ recommendations.
Off The job Training Methods:
1. Lectures:
Lecturing has several advantages. It is a quick and simple way to provide knowledge to large groups of trainees as when the sales force needs to learn the special features of a new product. You could use written materials instead, be they may require considerable more production expense and won’t encourage the give-and-take questioning that lectures do.
2. Programmed Learning:
Whether the medium is a textbook, computer, or the Internet, programmed Leering (Or programmed instruction) is a step-by-step, self-leaning method that consists of there parts.
1. Presenting questions facts or problems to the learner
2. Allowing the person to respond
3. Providing feedback on the accuracy of answers.
Generally, programmed learning presents facts ad follow-up questions. The learner can then respond, and subsequent frames provide feedback on the accuracy of his or hear answers. What the next question is often is often depends on the accuracy of the learner’s answer to the previous question. Programmed learning’s main advantage is that it reduces training. It also facilitates learning because. It lets trainees learn at their own pace, provides immediate feedback and (from the learner’s point of view) reduces the risk of error.
3. Audiovisual-Based Training:
Audiovisual-based training techniques like, PowerPoint’s, vide conferencing, audiotapes, and videotapes can be very effective and are widely used. The Ford Motor Company uses videos in its dealer training sessions to simulate problems and sample reactions to various customer complaints, for example.
Audiovisuals arc more expensive than conventional lectures hut offer some advantages. Of course, they usually tend to be more interesting. In addition, consider using them in the following situations:
1. When there is a need to illustrate how to follow a certain sequence over time, such as when teaching fax machine repair. The stop-action, instant replay, and fast- ar slow-motion capabilities of audiovisuals can be useful here.
2. When there is a need to expose trainees to events not easily demonstrable in live lectures, such as a visual tour of a factory or open-heart surgery.
3. When you need organization wide training and it is too costly to move the trainers from place to place.
4. Simulated training (occasionally called vestibule training) is a method in which trainees learn on the actual or simulated equipment they will use on the job, but are actually trained off the job. This is a necessity when it is too costly or dangerous to train employees on the job. Putting new assemblyline workers right to work could slow production, for instance, and when safety is a concern-as with pilots-simulated training may be the only practical alternative.
Simulated training may take place in a separate room with the same equipment the trainees will use on the job. However, it often involves the use of equipment simulators. In pilot training, for instance, airlines use flight simulators for safety’, learning efficiency, and cost savings, including sayings on.
5. Case Study: Case study method helps students to learn on their own by independent thinking. A set of data or some descriptive materials are given to the participants asking them to analyze, identify the problems and also tc5 recommend solutions for the same.
6. Role Playing: This training method particularly helps in learning human relations skills through practice and imbibing an insight into one’s own behaviors. Trainees of such a programmed are informed of a situation and asked to play their roles in the imaginary situation before the rest of the class. This therefore, helps in the enriching of interact Tonal skills of the employees.
7. T-Group Training: T-group is sensitivity training, and takes place under laboratory conditions and is mostly instructed and informal kind of training. The trainer in such a training program is catalyst. He helps the individual participants to understand how others perceive his behavior, how here acts to the behavior of others and how and when a group acts either in a negative or in a positive way.
8. E-learning: Training programmers delivered via intranet are now thought of as the most cost-effective route. It is not only cost effective but also caters to the real time information need of employees. However, it involves convergence of several technologies, like, hardware, software, web designing and authoring, instructional design, multimedia design, telecommunications and finally internet-intranet network management. Organization can outsource e-learning training modules at relatively cheaper rate. Even though training through e-learning is globally increasing, we do not have adequate empirical evidence to justify this.
Methods of Development:
Some development of an individual’s abilities can take place on the job. We will review several methods, three popular on-the-job techniques
1) Job rotation
2) Assistant-to position
3) Committee assignments
And three off-the jobs methods:
1) Lecturer courses and seminars
2) Simulation exercise
3) Outdoor training.
1) Job rotation:
Job rotation involves moving employees to various positions in the organization in an effort to expand their skills, knowledge, and abilities. Job rotation can be either horizontal or vertical. Vertical rotation is nothing more than promoting a worker into a new position. We will emphasize the horizontal dimension of job rotation, or what may be better understood as a short-term lateral transfer.
Job rotation represents an excellent method for broadening an individual’s exposure to company operations and for turning a specialist into a generalist. In addition to increasing the individual’s experience allowing him or her to exposure new information. It can reduce boredom and stimulate the development if new ideas. It can also provide opportunities for a more comprehensive and reliable evaluation of the employee by his or her supervisors.
2) Assistant-To positions:
Employees with demonstrated potential are sometimes given the opportunity to work under a seasoned and successful manager often in different areas of the organization. Working as staff assistants or, in some cases, serving on “special board,” these individuals perform many duties under watchful eye of a supportive coach. In doing so, these employee get exposure to a wide variety of management activities and are groomed for assuming the duties of the next higher level.
3. Committee Assignment:
Committee assignments can provide an opportunity for the employee to share decision making, to learn by watching others, and to investigate specific organizational problems. When committees are of a temporary nature, they often take on task-force activities designed to develop into a particular problem, ascertain alternative solutions, and make a recommendation for implementing a solution. These temporary assignments can be both interesting and rewarding to the employee’s growth. Appointment of permanent committee increase the employee’s exposure to other members of the organization, broadens his or her understanding, and provides an opportunity to grow a make recommendation under the scrutiny of other committee members. In addition on-the-job techniques described above, we will briefly discuss three of the more popular ones: lecture courses and seminars, simulations, and outdoor training.
1) Lecture course and seminars:
Traditional forms of instruction revolved around formal lecture courses and seminars. These offered an opportunity for individuals to acquire knowledge and develop their conceptual and analytical abilities. For many organizations, they were offered in house by the organization itself, through outside vendors, or both.
Technology is allowing for significant improvements in the training field. The use of digitized computer technology, a facilitator can be in one location giving a lecture, while simultaneously being transmitted over fiber-optic cable, in real time, to several other locations.
Over the past few years, we’ve witnessed an expansion of lecture courses and seminars for organizational members. This has been in the form of returning to college classes, either for credit toward a degree or by way of “continuing education” courses. Either way, the outcome is the same. Employees are taking the responsibility to advanced their skills, knowledge, and abilities in an effort to enhance their value-address to their current or “future” employer.
2) Simulations:
Simulations are probably ever more popular for employee development. The more widely used simulation exercises include case studies, decision games, and role plays.
The case-study analysis approach to employee development was popularized at the HarvardGraduateSchool of business. Taken from the experiences of organization, these causes represent attempts to describe, as accurately as posAIBL e, real problem that managers have faced. Trainees study the case to determine problem, analyze causes, develop alternative solutions, select what they believe to be the best solution, and implement it
Case studies can provide stimulating discussions among participants, as well as excellent opportunities for individual to defend their analytical and judgmental abilities. It appears to be a rather effective method for improving decision-making abilities within the constraints of limited information.
Simulated decision games and role-playing exercises put individuals in the role of acting out supervisory problem. Simulations, frequently played on a computer programmed, provide opportunities for individuals to make decisions and to witness the implications of their decisions on other segments of the organization.
Role playing allows the participants to act out problems and to deal with real people. Participants are assigned roles and are ask to react to one another as they would have to do in the managerial jobs.
3. Outdoor Training:
Outdoor training typically involves some major emotional and physical challenge. This could be whitewater rafting, mountain climbing, paint-ball games, or surviving a week in the ‘jungle.’ The purpose of such training is to see how employees react to the difficulties that nature presents to them. Do the face these dangers alone? Do they “freak”? Or are they controlled and successful in achieve their goals? The reality is that today’s business environment does not permit employees “stand alone”. This has reinforced the importance of working closely with one another, building trusting relationship, and succeeding as a member of a group.
Benefits for employees:
- The opportunity for promotion and self-improvement;
- Improved job satisfaction through better job performance
- A challenge: the chance to learn new things;
- Adaptability: greater ability to adapt to and cope with changes
- Increase job scope and allow for job rotation
Benefits for the organization:
- Higher productivity through better job performance, more efficient use of human resources;
- Goals and objectives more effectively met;
- Reduced costs due to less labor turnover, errors, accidents etc.
- A more capable, mobile workforce;
- Existing staff more easily retained; An insurance policy; employees are better able to cope with organization
Training institutes of Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited :
Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited training institution was established in 1996. Since then, institute has been conducting various types of training programs on different banking affairs in order to develop knowledge, skip; and attitude of the employees of bank.
The major objectives are:
¨ To enrich both theoretical and practical knowledge in banking and also developing managerial skills of the employees of bank.
¨ To impact training programs based can day-to-day banking needs.
¨ To raise the standard of performance of the work force employed in the bank.
Officers/staff trained since it’s inception
Year No. of officers’/staff
1996 500
1997 1000
1998 1200
1999 1300
2000 800
TRAINING PERFORMANCE (2001-2009)
The Training Institution plays a significant role in the field of training of officers and staff members of the bank. Under different banner of the training courses in 64 batches a total number of 4399 Officers and Executives have already been imparted training
Year | Number of courses | Number of participant (Yearly basis) |
| 2001 | 25 | 291 |
| 2002 | 32 | 300 |
| 2003 | 35 | 450 |
| 2004 | 39 | 425 |
| 2005 | 40 | 425 |
| 2006 | 40 | 500 |
| 2007 | 33 | 525 |
| 2008 | 42 | 530 |
| 2009 | 40 | 550 |
Total | 326 | 3996 |
Training Performance-2009:
Sl. no: | Name of course | Level of participants | Frequency | Number of participants |
| 1 | Foreign Exchange & Foreign trade | Officer to SPO | 1 | 31 |
| 2 | Branch Management | Sr. Officer to SPO/Br. manager | 1 | 26 |
| 3 | Banking foundation Course | Officer | 2 | 66 |
| 4 | Human Relation & Communication Development | Sr. Officer to SPO/Br. Manger | 1 | 30 |
| 5 | Internal Control &Compliance | Officer to SPO | 2 | 60 |
| 6 | Credit Management | Officer to SPO/ Manager | 2 | 48 |
| 7 | Banking foundation Course (Newly-Recruited IT Personnel) | FT Personnel | 5 | 47 |
| 8 | Basic Accounting & Al-Arafah Bank Accounting Personnel | Officer to PO | 1 | 29 |
| 9 | Audit , Inspection & Implementation | Audit officer | 2 | 55 |
| Sub-total | 17 | 392 |
Workshops :
Sl no. | Name of Workshop | Level of participants | Frequency | Number of participants | ||
| 1 | Money Laundering Prevention | Executives/ Br. Managers’ Concerned Officers | 5 | 137 | ||
| 2 | Core Risk Management : Asset Liability Management | Selected Executives.’ Officers | 1 | 34 | ||
| 3 | Core Risk Management : Internal Control & Compliance | Selected Officers | 1 | 3S | ||
| 4 | Core Risk Management :Credit Risk Management | Selected Officers | 1 | 40 | ||
| 5 | Recovery of Classified Advances. De-classification and Suit Settlement Techniques | Officers to SPO (Branch Manager Credit Officer) | 2 | 69 | ||
| 6 | Trade Financing : SME & Consumer Financing | Officer to SPO (Branch Manager Credit Officer) | 1 | S3 | ||
| 7 | International Accounting Standard (IAS-30) | Officer to SPO (Concerned Officer) | 1 | 26 | ||
| 8 | Management of non-performing assets & techniques of profitability | Officer to SPO( Branch Manager/Credit Officer) | 2 | 67 | ||
| 9 | Performance Management & Discipline : Conducting Inquiry | Selected Officers of Disciplinary Action Division. Zones Circles Corp.Br. | 1 | 28 | ||
| 10 | Reporting on foreign trade Transaction | ID & AD branch dealing officer | 1 | 57 | ||
| 11 | Name of Workshop | Level of participants | Frequency | Number of participants | ||
| 12 | Credit Risk Grading | Officer to SPO (credit officer | 4 | 134 | ||
| 13 | Procedure of loan classification and preparation of cl statements | Officer to SPO (branch manager) | 3 | 93 | ||
| 14 | Al – arafali bank audit implementation manual | Audit officer | 2 | 40 | ||
| 15 | BASEL- 11 ACCORD | Senior Executives (D.V1D. EVP,SVP,VP) | 1 | 25 | ||
| 16 | Short orientation course on Foreign Exchange &Foreign trade) | Concerned officer | 1 | 32 | ||
| 17 | Senior management development programmed | Senior Executives (DMD and EVP) | 1 | 13 | ||
Sub- total : |
| 35 | 838 | |||
COMPUTER COURSES :
Sl No | Name of course | Level of participants | Frequency | Number of participants |
| 1 | Computer : PC-MS Office (Officer) | SO/Officer | 3 | 81 |
| 2 | Computer Literacy and English language (clerical) | Clerical staff | 2 | 54 |
| 3 | Computer : Application and operation of branch banking software (Day) | Branch Manager Officer (Outside Dhaka) | 4 | 67 |
| 4 | Computer : Application and operation of branch banking software (Evening) | Branch Manager. Officer Dhaka | 6 | 55 |
| 5 | Computer : branch banking operation (Audit) | Audit officer | 2 | 36 |
| 6 | Computer : Application & operation of Zonal office software (Day) | Concerned officer (outside Dhaka) | 7 | 120 |
| 7 | Computer ; Application &Operation of Zonal office software (Evening) | Concerned officer (Dhaka) | 35 | |
| 8 | Computer : MIS in AL-ARAFAH bank (Day) | Concerned officer (outside Dhaka) | I | 1? |
| 9 | Computer : MIS in Al-arafah Bank (Evening) | Concerned officer (Dhaka) | 2 | 30 |
| 10 | Programming in COBOL (Evening) | Concerned officer | 1 | 16 |
| 11 | Zonal office solution | Concerned IT officer | 1 | 57 |
Total | 88 | 568 |
TRAINING PERFORMANCE – 2009 :
Products and services include:
Cash management.
Wire transfer
Automated clearinghouse (ACH) transactions.
Bill presentment and payment.
Balance inquiry.
Funds transfer.
Downloading transaction information.
Loon applications.
Investment activity.
Other value-added services.
In line with the Banks strategy of making banking services more accesAIBL e to customers AIBL is planning to launch proper Banking Services and Business in all its branches. Part of these are ATM services, Internet Banking services. SMS Banking services. Online Utility Bill Payment Services etc.
Inshallah the Bank will very soon launch ATM services taki8ng a step further towards fully online Bank The Bank is proud to announce to be a part of Central Banks pilot project of the automated clearing house which involves only the top Bank’s of the country with frue centralized Banking Systems.
The Bank has also shook hands with El Dorodo project a private Automated Clearing house as pioneer partner. The project is approved by the Central Bank and is the first of its kind in Bangladesh.
To sum up Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited in a very short span of period has achieved what many other bands have been striving for ever a much longer period.
Performance Evaluation and Performance Reward
The Human Resource Division plays strategic role in the development of Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited and finds them focusing strategies that will align with the strategic business needs and priorities of the bank. HRD is managing a large number of employees which is a challenging task and requires efficient handling. HRD delivers day to day operational support to its employees so that employees are being satisfied and believe that as an employer “Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited ” do care to its employees”. And later on they perform according to the business needs.
From the above data, it has been found that employees of Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited Bangladesh are very much satisfied about training and development process provided by the bank. HRD always evaluate performance through observation, work output, strength and than reward employees according to their excellent performance. They select and reward employee on the basis of month and sometimes quarterly performance based.The following charts shows employee strength and trained up employee strength of the Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited.
Here, I have assumed a sample of 6000 employees of Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited Day by day Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited investing a huge amount of money to train their employees so that they can be more skilled, increase their strength and perform up to the mark. Here, each year employees strengths are increasing and this is fact they are performing outstanding than before.
Audit and Inspection:
The Audit & Inspection Department of ICCD has been adequately staffed by experienced manpower. To detect operational deficiences / lapses / irregularities and reducing of the different risks of banking functions. AIBL conducts regular Audit & inspection on all the branches & department/division of HO of the Bank as per rules/ guidelines of regulatory authorities and Internal
Audit manual/ Risk management guidelines/ operation manuals /instruction Circulars etc.
Types of Audit & Inspections are undertaken by Audit & Inspection Department:
a) Risk based Comprehensive Audit & inspection all the branches once in a year.
b) Auditing of Branches handling Foreign Exchange & Foreign Trade-quarterly basis.
c) Surprise Inspection-at regular intervals.
d) Auditing of each Division /Deptt. of Head Office once in a year.
Nature of Inspection No of branches/division:
Comprehensive & Risk Based
Internal Audit & Inspection 50 (Branches)
Surprise Inspection 06 (Branches)
In 2008, the Inspection Teams of Bangladesh Bank have inspected different branches & Head Office and also conducted Special Inspection on 06 Core Risk areas in banking. In addition, Bangladesh Bank also conducted Special Inspections in different branches/departments at Head Office.
Rating Report:
As per Bangladesh Bank Guidelines we have got rated by Credit Rating Agency of Bangladesh (CRAB). In the year 2007 the long term and short term grading were A3 and ST-2 respectively.
Conclusion:
As an organization the Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited has earned the reputation of top banking operation in Bangladesh. The organization is much more structured compared to any other bank operating local or foreign in Bangladesh. It is relentless in pursuit of business innovation and improvement. It has a reputation as a partner of consumer growth.