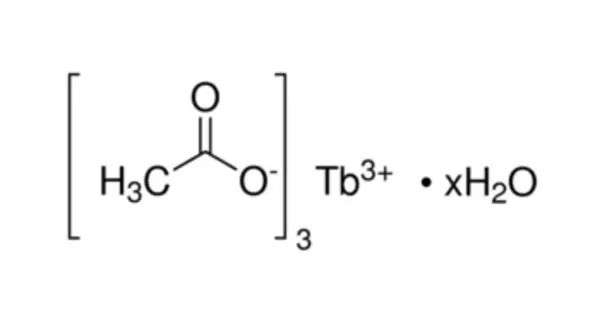
Terbium(III) acetate is the acetate salt of terbium, with a chemical formula of Tb(CH3COO)3. It is not typically found in nature but is synthesized for its specific uses in various technological and scientific applications. It is a rare earth metal salt where terbium is in the +3 oxidation state.
It is used as a dopant in phosphors for fluorescent and phosphorescent materials due to its luminescent properties. It can act as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions.
Physical properties
The tetrahydrate of terbium acetate can lose hydration at 60 °C, obtaining the anhydrate at 180 °C, which starts to decompose at 220 °C, forming terbium oxide at 650 °C.
- Chemical formula: Tb(CH3COO)3
- Appearance: White crystals
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 284.3 g/mol
- Solubility: Soluble in water, forming a solution with a slightly acidic pH.
- Stability: Relatively stable under normal conditions but should be stored in a dry environment to prevent decomposition.
Occurrences
- Laboratory Synthesis: Terbium(III) acetate is usually synthesized in the laboratory from terbium(III) oxide or terbium(III) chloride through a reaction with acetic acid.
- Research: It is used in research and industry as a reagent for various applications, including in the production of other terbium compounds and in materials science.
- Materials Science: Terbium(III) acetate can be used in the preparation of terbium-based phosphors and in other applications where terbium’s unique electronic and optical properties are required.
Applications
- Phosphors: Used in the production of phosphorescent materials.
- Catalysts: Employed in some catalytic processes.
- Optical Devices: Utilized in optical materials due to terbium’s fluorescence properties.