A solar vehicle is a vehicle that is powered by energy from the sun, typically through the use of solar panels. These vehicles can be used for a variety of purposes, including transportation, recreation, and competitions. They can be designed for use on land, in the air, or on water. Some solar vehicles are designed to be used as a primary mode of transportation, while others are built for specific events such as solar car races. They are considered as a sustainable mode of transportation as they do not emit any pollutants and are dependent on renewable energy source. This electricity is then used to power an electric motor, which drives the vehicle.
Solar vehicles are typically more environmentally friendly than traditional gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles, as they produce no emissions and rely on a renewable energy source. However, they may have limitations in terms of range and performance, as they are dependent on the availability of sunlight. Solar vehicles can be used for transportation, recreation, and racing, and they have the potential to be a clean and sustainable source of transportation in the future. However, they are currently limited by the cost and efficiency of solar cells, as well as the need for additional energy storage solutions.

Solar vehicles can be used for transportation, as well as for other applications, such as powering homes and businesses. They are a clean and sustainable form of transportation, as they do not produce emissions and rely on a renewable energy source.
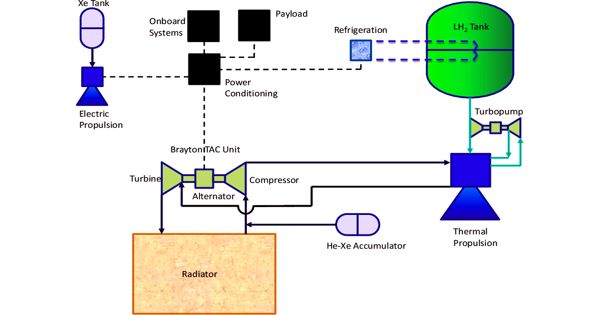
A solar vehicle, also known as a solar electric vehicle, is an electric vehicle that is powered entirely or primarily by direct solar energy. Photovoltaic (PV) cells in solar panels typically convert the sun’s energy directly into electric energy. The term “solar vehicle” usually implies that solar energy is used to power all or part of the propulsion of a vehicle. Solar power can also be used to power communications, controls, and other auxiliary functions.
Solar vehicles are currently sold as demonstration vehicles and engineering exercises, often sponsored by government agencies, rather than as practical day-to-day transportation devices. However, indirectly solar-charged vehicles are common, and solar boats are commercially available.