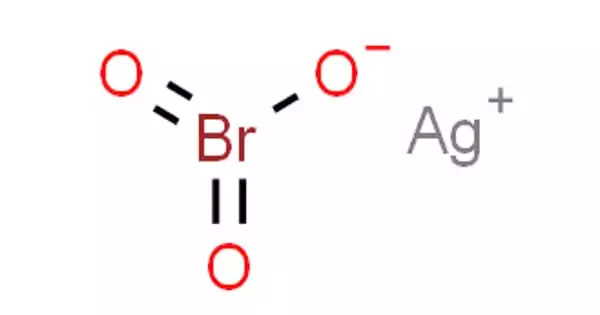
Silver bromate (AgBrO3) is a poisonous white powder that is light and heat sensitive. It is an inorganic chemical compound of silver that belongs to the bromate group. Bromine, with the symbol Br and atomic number 35, is a halogen element. Although diatomic bromine does not exist in nature, bromine salts can be discovered in crustal rock. Silver is a metallic element with the atomic number 47 and the chemical symbol Ag. It can be found in its pure, unaltered form, as an alloy with gold and other metals, and as minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite.
Properties
It’s a white, light-sensitive solid that’s not very soluble in water. When heated, it decomposes. He possesses a space group I4 / m tetragonal crystal structure (a = 860 pm, c = 809 pm, Z = 8). It is distinguished by its photosensitivity (absorbs energy from light). When exposed to light, it reacts by turning grey or black. As a result, it must be kept in the dark. It rapidly interacts with liquid ammonia to generate a variety of amine complexes. Under normal settings, it is a stable substance, but when heated to high temperatures, it decomposes, releasing deadly bromine gases.
- Molecular Weight: 235.77
- Appearance: solid
- Form: white tetragonal crystals
- Melting Point: N/A
- Boiling Point: N/A
- Density: 5.206 g/cm3
- Solubility in H2O: N/A

Occurrence
Silver bromide occurs naturally as the mineral bromargyrite in considerable amounts. However, it is typically obtained in large amounts through chemical production.
Uses
As an oxidant, silver bromate can be used to convert tetrahydropyranyl ethers to carbonyl compounds. It is used in the production of photographic films and plates. It is also employed in infrared applications, as well as light-sensitive spectacles and semiconductors. It has antiseptic qualities and is used as a topical disinfectant and astringent, similar to other silver halides.
Health effects
It is not a particularly dangerous substance. It, like many other silver compounds, can cause irritation and greyish discoloration when it comes into contact with the skin or eyes. Sneezing, coughing, and trouble breathing can occur as a result of inhalation. Swallowing significant amounts can discolor tissue and harm the central nervous system and kidneys.