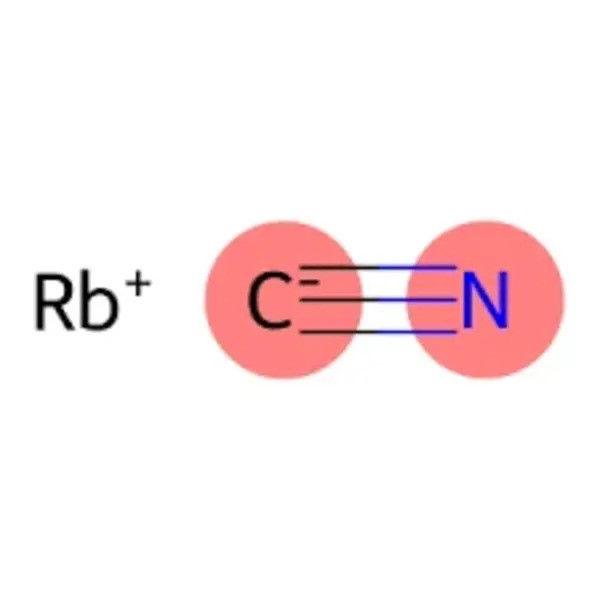
Rubidium cyanide (chemical formula: RbCN) is the rubidium salt of hydrogen cyanide. It is a salt formed from rubidium hydroxide and hydrogen cyanide. It is a white solid, easily soluble in water, with a smell reminiscent of bitter almonds, and somewhat similar in appearance to sugar. Rubidium cyanide has chemical properties similar to potassium cyanide, and is similarly very toxic. It is typically used in chemical research and has applications in various fields, including materials science and organic chemistry.
Production
Rubidium cyanide can be synthesized by the reaction of hydrogen cyanide and rubidium hydroxide in alcohol or ether: HCN + RbOH → RbCN + H2O.
Properties
- Chemical formula: CNRb
- Molar mass: 111.486 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White solid
- Solubility: Rubidium cyanide is soluble in water.
- Density: It has a density of around 2.13 g/cm³.
- Melting Point: It has a melting point of approximately 1500 °C (2732 °F).
Reactivity
Like other cyanides, it is highly reactive and toxic. It reacts with acids to release hydrogen cyanide (HCN), which is a highly toxic gas.
Occurrences
Natural Occurrence: Rubidium cyanide is not found naturally. It must be synthesized in the laboratory.
Industrial Use
It is used in research and some specialized applications, but it is not a common compound in industrial processes.
Safety
Due to its cyanide content, it is handled with caution, and proper safety measures are required to avoid exposure and contamination. It is part of the broader category of alkali metal cyanides, which are known for their strong reactivity and potential hazards.