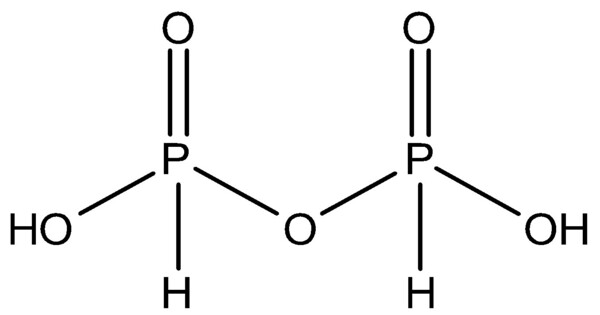
Pyrophosphoric acid, also known as diphosphoric acid, is the inorganic compound with the formula H4P2O7 or, more descriptively, [(HO)2P(O)]2O. It is typically a colorless, viscous liquid in its pure form, but it can also be encountered as a crystalline solid. It is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. Colorless and odorless, it is soluble in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol.
Pyrophosphoric acid is a stronger acid than phosphoric acid but weaker than phosphonic acid. It can react with bases to form pyrophosphate salts. The anhydrous acid crystallizes in two polymorphs, which melt at 54.3 and 71.5 °C. The compound is a component of polyphosphoric acid, an important source of phosphoric acid. Anions, salts, and esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates.
Properties
It is a colorless, viscous liquid. It is highly soluble in water, forming phosphoric acid in aqueous solutions. It is a strong acid, though not as strong as phosphoric acid. Its acidity is due to the presence of two phosphoric acid groups connected by an oxygen bridge.
- Chemical formula: H4P2O7
- Molar mass: 177.97 g/mol
- Melting point: 71.5 °C (160.7 °F; 344.6 K)
- Solubility in water: Extremely soluble
- Solubility: Very soluble in alcohol, ether
- Conjugate base: Pyrophosphate
Preparation
It can be prepared by reaction of phosphoric acid with phosphoryl chloride:
5 H3PO4 + POCl3 → 3 H4P2O7 + 3 HCl
It can also be prepared by ion exchange from sodium pyrophosphate or by treating lead pyrophosphate with hydrogen sulfide.
Boiling the water from orthophosphoric acid will not dehydrate it to pure pyrophosphoric acid, instead a mixture of ortho, pyro, and polyphosphoric acids are produced, the maximum pyrophosphoric acid concentration remains below 50% and occurs slightly before what would otherwise be pure pyrophosphoric acid.
Uses
It’s used in various chemical and industrial applications, including in the synthesis of organophosphates and as a reagent in chemical analysis.
- Chemistry and Biochemistry: It’s used in various chemical processes and reactions. It can act as a reagent in some biochemical applications.
- Buffer Solutions: It is used to prepare buffer solutions in analytical chemistry.
- Pharmaceuticals and Detergents: It has uses in the pharmaceutical industry and in the formulation of detergents and cleaners.