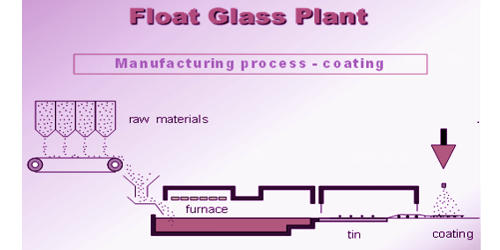
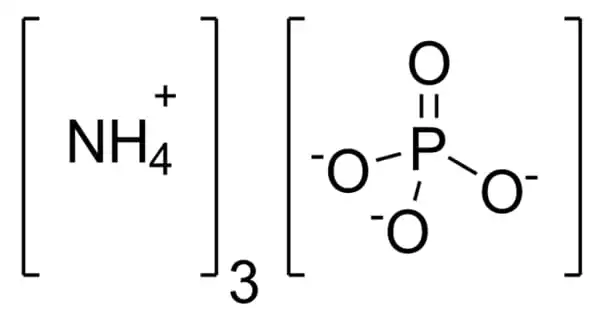
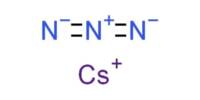Pyrolytic coatings are metallic oxides applied during the float manufacturing process, while the glass is still in a semi-molten state. It is a thin film coating applied at high temperatures and sprayed onto the glass surface during the float glass process. The coating becomes a permanent part of the glass, increasing the durability and toughness. Pyrolytic glass is also referred to as “hard-coat” glass.
It is a thin, metallic, reflective film coating applied at high temperatures and sprayed onto the glass surface during the float glass process in the manufacturing of architectural glass products. It is suggested that various non permanent protective films be used at construction sites to protect the window surfaces during storage and when they are installed on the building.
Advantages
- Relatively durable coating.
- Can be tempered after coating application.
- Can be used in single glazing applications.
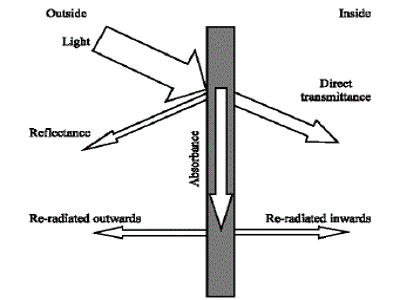
Fig: Energy-Efficient Optical Coating for Flat Glass
Applications
The pyrolytic coating can be used as a protective or decorative coating on equipment parts, energy-insulator on window glasses, an anti-friction agent in molding applications. Pyrolytic coated architectural glass is usually present in a reflective glass curtain wall and window in buildings built before 1980.
Coating blemishes are an inherent part of the glass-coating process. In addition, coatings can be damaged as a result of improper transportation, storage, handling, fabrication, or installation. Individual manufacturers should be contacted for recommended handling, fabrication, installation, and application guidelines. Especially in certain parts of the world where very large structures are constructed in actual deserts where the temperature soars during the day.